Sperm passage
SEVEN UP
- Seminiferous tubule
- Epididymis
- Vas Deferens
- Ejaculatory ducts
- N (nothing)
- Urethra
- Penis
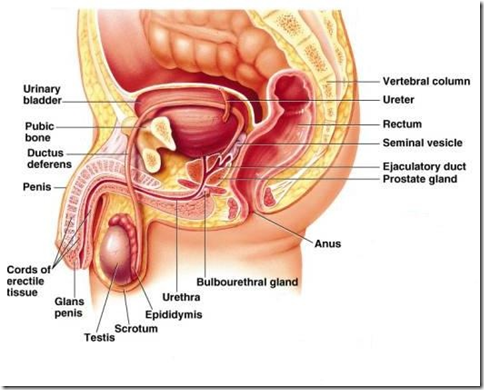
Testes
- situated in the scrotum
- 2 covering
- tunica vaginalis
- parietal & visceral layer
- in between the layer: thin cavity with little fluid
- tunica albugenia
- fibrous capsule
- thickened posteriorly (mediastinum)
- septa divides the testis into lobules
- 250-300
- Functions
- spermatogenesis
- secretion of testosterone
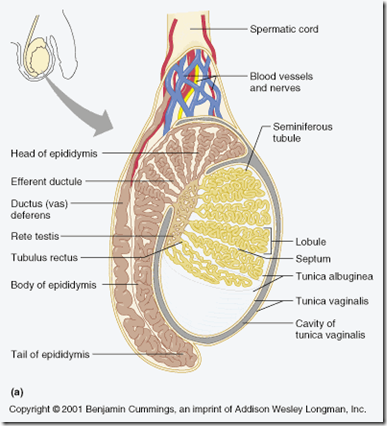
Seminiferous tubules
- highly convoluted
- situated within lobules
- Lined by germinal epithelium
- spermatogonium
- primary & secondary spermatocyte
- early & late spermatids
- spermatogenesis –> mature spermatozoa
- Opens to rete testes in the mediatinum
Image: Spermatogenesis
Sertoli cells/ Sustentacular cells
- form the blood testis barrier
- important because sperms are considered as foreign bodies
- if enter blood, antibodies will kill it
- supply nutrients
- secrete testicular fluid
- phagocytosis
Interstitial cells/Leydig’s cells
- lies in between seminiferous tubules
- secretes testosterone
_____________________________________________________________________Duct system
- epididymis
- long highly coiled tubule
- lies on posterior surface of the testis
- divided into head, body & tail
- efferent ductules open to head
- tail continuous with vas deferens
- Function:
- capacitates sperms
- supplies nutrients to sperms
- stores sperms
- removes dead sperm
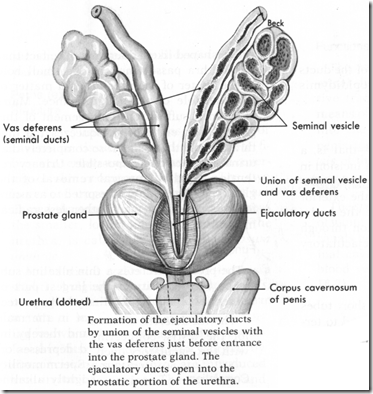
- vas deferens
- from tail of epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts
- part of it in scrotum, part of it in pelvic cavity
- very thick muscular wall with small lumen
- Functions:
- propels sperms during ejaculation
- peristalsis of smooth muscles
- ejaculatory duct
- formed by union of vas deferens & duct of the seminal vesicle
- passes through prostate gland
- opens to the urethra
- urethra (passage for urine & semen)
- prostatic
- midline urethral crest
- prostatic sinuses on either sides
- ejaculatory ducts open to seminal colliculus on the urethral crest
- prostatic ducts open to prostatic sinuses
- membranous
- penile
Accessory glands
- Seminal vesicle
- located behind the bladder & above the prostate
- join the vas deferens to form the ejaculatory ducts
- 60% of seminal fluid
- yellowish, viscous & alkaline
- fructose & ascorbic acid
- coagulating enzyme (vesiculase)
- prostaglandins
- Prostate gland
- lies inferior to bladder
- urethra & ejaculatory ducts passes through it
- several ducts open to prostatic urethra
- thich capsule
- secretory unit embedded in a fibro-muscular stroma
- secretions
- acidic (citrate)
- fibrinolysins
- hyaluronidase
- acid phosphatase
- prostaglandins
- PSA (prostate specific antigen)
- Bulbo-urethral glands (Cowper’s glands)
- lie inferior to prostate gland
- ducts open to penile urethra
- secretes
- pure mucus
- just before ejaculation to neutralise acidity of urine
_____________________________________________________________
External genitalia
Scrotum
- sac of skin & superficial fascia
- midline septum
- hangs from root of the penis
- testes suspended in it
- provides optimal temperature for spermatogenesis
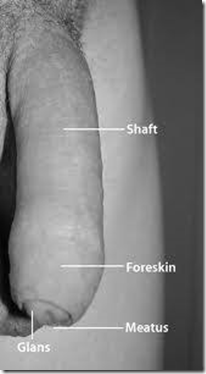
Penis
- Root
- Shaft
- skin over shaft is loose
- forms a cuff over glans (prepuce)
- Glans
- urethral opens to exterior (vertical slit)
Structure of the penis
- 3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue
- 2 corpora cavernosa
- lies on both sides of the corpus spongiosum
- proximal part covered with ischiocavernous muscles
- 1 corpus spongiosum
- expands distally to form the glans
- whole length covered with bulbospongeosus muscle
- Penile urethra passes through it
- Functions:
- copulation (sex)
- passage of urine & sperm