*Read foundation 1 notes
Visual system
- Eye
- image formation & phototransduction
- Visual pathway
- tranmission of nerve impulses
- Visual cortex
- occipital lobe of cerebral cortex
- primary visual receiving area: sides of the calcarine fissure
- visual processing & perception occurs here
Stimulus
- Light
- visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
Sensory organ
- Eye
- optical instrument for focusing of images on retina by refraction of light rays
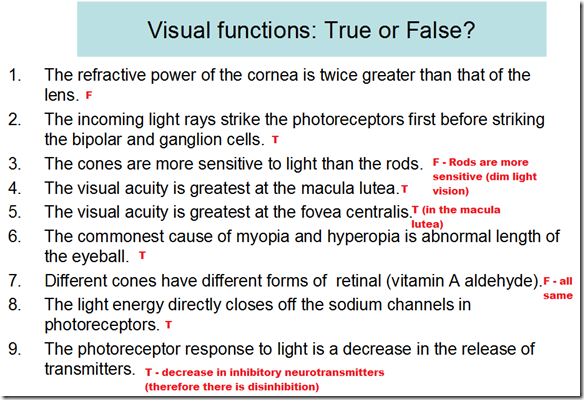
- Refractive power
- Cornea: 40 dioptres
- fixed
- Lens: 20 dioptres
- adjustable
- Photoreceptors on retina
- rods
- cones
_____________________________________________________________________
Refraction of light
- when light beam passes through an angulated interface, light rays bend
- measured in diopters
- Biconvex spherical lens
- convergence
- Concave spherical lens
- divergens
Accommodation
- Parasympathetic response
- When a person looks at a near object, 3 changes occur:
- accommodation reflex
- convergence of visual axis
- pupil constrict
- When accommodation relaxed:
- Near object (<6 m)
- diverging rays
- image falls behind retina
- Far object (>6 m)
- parallel rays
- image falls on retina
- Physiology
- ciliary muscles contracts
- this relaxes the lens ligaments
- lens spring into a more convex shape
- near point of vision recedes throughout life
- slowly at 1st
- advancing rapidly with old age
- due to increasing hardness of lens
- impaired accommodation
- receding of near point
- Presbyopia
- reading and close vision difficult
- corrected by wearing convex lens
- diverging rays
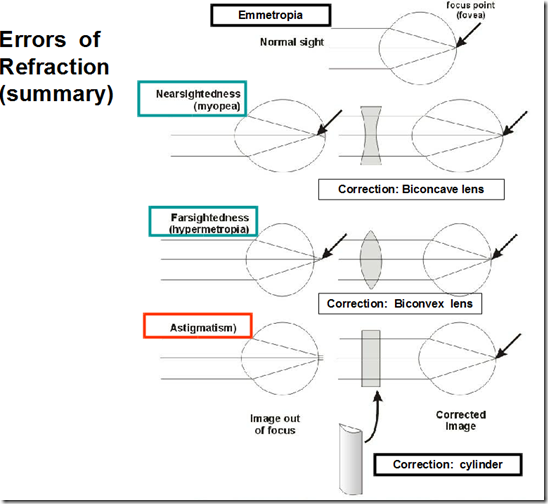
- Errors of refraction
- Emmetropia
- normal vision
- accommodation relaxed
- far object, parallel rays – image falls on retina
- Hyperopia
- farsightedness
- short eyes ball/weak lens
- image from distant objects formed behind retina
- accommodation all the time
- ciliary muscle overworked
- eye strain
- headache
- convergence of visual axes
- squint/strabismus
- corrected by
- convex lens
- Myopia
- nearsightedness
- long eye ball
- image from distant objects is formend infront of retina
- corrected by
- concave lens
Astigmatism
- Uneven corneal surface
- curvatures at various meridians not equal
- Different focal points
- distorted image
_____________________________________________________________________
Photoreceptors
- Receptor cells containing excitatory/inhibitory synaptic transmitters
Rods
- Photopigments
- protein: rhodopsin
- Vitamin A aldehyde
- retinal
- retinene
- Abundant in
- peripheral retina
- Low threshold receptors for
- dim light
- night vision (scotopic vision)
- Most sensitive to
- 505 nm
- Blue-Green
Cones
- Photopigments
- protein: photopsins
- Vitamin A aldehyde
- retinal
- retinene
- Abundant in
- central retina
- particularly in fovea centralis (in macula lutea)
- Higher threshold receptors for
- daylight
- detailed vision (photopic vision)
- colour vision
- Visual acuity greatest at
- fovea centralis
Phototransduction
In the photoreceptors,
- In the dark
- Na+ channel open
- Na+ entry
- Depolarization
- Inhibitory neurotransmitter release
- Bipolar cells inhibited
- Ganglion cells (axons of optic nerves)
- decrease discharge
- In the light
- Activates rhodopsin
- decomposition of rhodopsin
- cis-retinal bleached –> trans-retinal (opsin & retinal)
- retinal detaches from opsin
- activated opsin
- Na+ channels close
- Na+ entry decrease
- Hyperpolarization
- Decrease inhibitory neurotransmitter release from the rod
- removal of inhibition
- Bipolar cells excited
- Ganglion cells
- action potential initiated
- transmit to the brain –> vision occurs
Dark adaptation
- If one moves from a brightly lighted room to a dimly lighted room
- retina slowly becomes more sensitive to light
- pupil dilate – to capture more light into the retina
- this decline in visual threshold: dark adaptation
- Dark adaptation depends on
- rate of regeneration of rhodopsin
- which depends on vitamina A (retinol)
- Vitamin A deficiency:
- Signs & Symptoms
- impaired dark adaptation
- Nactalopia
- night blindness
- Bitot spots
- Xerophthalmia
- eye drying
- Keratomalacia
- corneal softening
- Ulceration
- Scars
- Pathophysiology
- degeneration of rods & cones
- degeneration of neural layers of retina
- blindness
- most common cause of preventable blindness
- treatment before receptors are destroyed
_____________________________________________________________________
Colour vision
- The sensation of white/any spectral colour can be produced by
- mixture of various proportions of
- Red wavelength
- Green wavelength
- Blue wavelengh
- 3 types of cones
- Red cones
- absorb long wavelength, L cones
- Green cones
- absorb medium wavelength, M cones
- Blue cones
- absorb short wavelength, S cones
- Cones most sensitive to
- 405 nm (yellow-green)
Color blindness
- Trichromats (have 3 cone systems -RGB)
- Normal trichromats
- individuals with normal colour vision
- Anomalous trichromats (1 weak cone system)
- Protanomaly
- red weakness
- defective red-sensitive cones
- Deuteranomaly
- green weakness
- defective green-sensitive cones
- Tritanomaly
- blue weakness
- defective blue-sensitive cones
- Dichromats (2 cone systems)
- Protanopia
- red blindness
- no red-sensitive cones
- Deuteranopia
- green blindness
- no green-sensitive cones
- Tritanopia
- blue blindness
- no blue-sensitive cones
- Monochromats (1 cone system)
- Causes of colour blindness
- Inherited
- X-linked recessive
- defective opsins
- most frequently: red-green weakness
- Lesions of visual cortex concerned with colour vision
- achromatopsia
- Sildenafil (viagra)
- inhibits retinal as well as penile form of phosphodiesterase
- transient blue-green colour weakness
Test for colour vision
- Colour matching
- Ishihara Pseudoisochromatic plates
_____________________________________________________________________
Visual fields & Visual pathways
- Fusion of 2 images occurs in the visual cortex
- Visual axes of 2 eyes must be properly aligned
- if not, double vision (diplopia)
- Diplopia
- 2 different images sent to the brain
- brain will suppress one of the images
- to prevent seeing double
- in children (<6 y/o)
- suppression of one eye’s input to the brain leads to reduced vision in the suppressed eye
- amblyopia
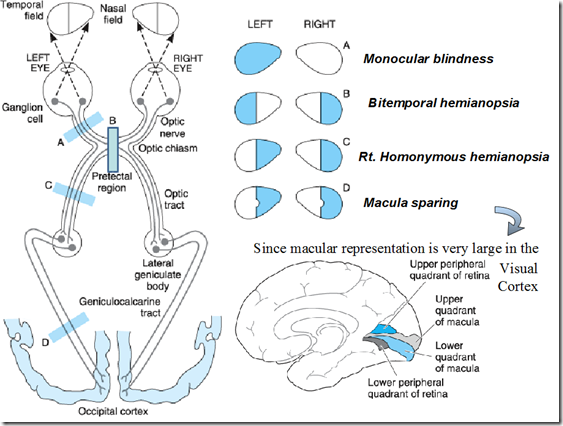
- Examination of visual fields
- Perimetry
Lesions in visual pathways (Visual field defect)
- Anterior pituitary tumours
- pressure on optic chiasma from below
- eg. visual field defects in gigantism
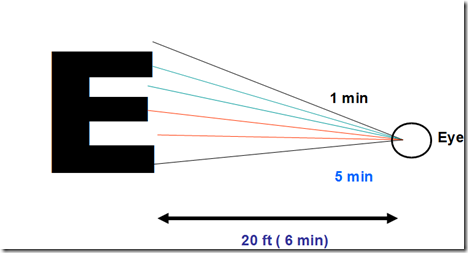
Visual acuity
- Defined in terms of minimum separable
- shortest distance by which 2 lines can be separated & still be perceived as 2 lines
- corresponds to a visual angle of about 1 minutes
- Snellen letter charts
- designed so that the height of the letters in the smallest line a normal individual can read at 20 ft (6m) subtends a visual angle of 5 minutes
- Jaeger’s cards
- test for near vision (reading)
- When visual acuity is markedly reduced
- can be quantified in terms of
- Count fingers (CF)
- distance at which the patient can count fingers
- Hand movement (HM)
- discern hand movement
- Perceive light
- No light perception (NLP)
- if an eye is totally blind, examination will reveal NLP
_____________________________________________________________
Blindness (Visual impairment)
- Transient blindness
- may occur on sudden exposure to darkness/bright light
- blinding light
- light adaptation= 5 minutes
- Transient monocular blindness
- associated with an increased risk of subsequent stroke
- Night blindenss
- Colour blindness
- Total blindness
- Visual field contraction/blindness
- Legal blindness
- a level of visual impairment that has been defined by law to determine eligibility for benefits
- central visual acuity of 20/200 or less
- in the better eye
- with best possible correction
- visual field of 20 degrees or less
Common causes of blindness
- Cataract
- Lens opacity increases
- due to aging
- leading cause of blindness
- Glaucoma
- increased accumulation of aqueous humor
- increased pressure in anterior & posterior chambers
- increased pressure on vitreous humor
- increased pressure on retinal layers & optic nerve
- Age-related macular degeration (AMD)
- trachoma (infection)
- other corneal opacities
- diabetic retinopathy
- retinal detachment
- Eye conditions in children
- cataract
- retinopathy of prematurity
- vitamin A deficiency
- amblyopia
- associated with refractive error/strabismus/squint
_____________________________________________________________________









good
information in a capsule .good
very good
i am satisfied by your lecture note.
nice and good notes
brief and precise
perfect
Magnificent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you are just too fantastic.
I actually like what you have acquired here, really like what you’re saying and the way in which you say it.
You make it enjoyable and you still care for to
keep it wise. I cant wait to read far more from
you. This is actually a great site.
Great overview. Of the visual system Forrest student
very nice presentation
good post… keep it on top