Read from Dr. Chen Yu Sui’s notes
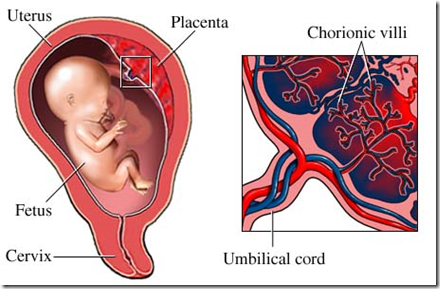
Umbilical cord
- 2 arteries & veins entwined
- surrounded by mucopolysaccharide substance
- Wharton’s Jelly
Amnion
- Fused with chorion at end of 2nd month
- No blood & nerve supply
Chorion
- Inner aspect: in contact with amnion
- Outer ascpect: in contact with maternal decidua
- No blood & nerve supply
- Cotyledon (lobule)
- forms a unit which contains a main chorionic villous tree
Decidua basalis
- non glandular, non vascular cells of the endometrial CT
- produced by steroid-dependent division & differentiation of maternal uterine stromal cells
_____________________________________________________________________
Placentral functions
Maintenance of pregnancy
- Human Placental hCH
- acts on corpus luteum
- prevent luteolysis
- stimulate progesterone production
- acts on placenta
- enhance conversion of maternal LDL cholesterol to pregnenolone & progesterone
- Regulate development of foetal adrenal & gonad
- during 1st trimester
- Suppression of maternal immune system
- prevent rejection of fetus
- As tumour marker
- Plactental Lactogen (hPL)/ chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)
- Similar features to GH & prolactin
- alter maternal glucose metabolism & lipolysis
- Causes hyperinsulinemia due to glucose load
- stimulate insulin secretion
- prolonged hyperinsulinemia
- peripheral insulin receptor resistance
- decrease glucose utilisation
- diverts glucose to fetus
- Placental progesterone
- Independent of factors
- not influenced by pituitary hormones
- increased when placental hCG drops
- blockade of myometrial prostaglandins production
- reduce uterine contractility
- stimulate endometrial gland secretion
- Inhibit ovulation
- prevent FSH secretion
- Immunosuppressant
- inhibit fetal rejection
- Placental oestrodiol
- DHEA-sulphate from foetal adrenal gland
- human placenta does not have 17-alpha hydroxylase
- converted to DHEA by placental sulfatase
- Growth of myometrial smooth muscles
Nutrient transport
- Placenta act as surrogate
- lung
- gut
- kidney
- Nutrients cross interhaemal barrier by 3 mechanisms:
- Passive/simple diffusion
- lipid soluble molecules
- O2, CO2
- urea
- fatty acids
- drugs (aspirin)
- Facilitated diffusion
- hydrophilic solutes
- D-glucose
- lactate
- Active transport
- amino acids
- Ca
- Mg
- Iodide
- Iron
- PO4
- Vit A & C
Factors affecting rate of diffusion:
- blood flow rates
- foetal villous exchange total surface area
- distance of diffusion
- syncytial trophoblast
- capillary endothelium
- concentration gradient
_____________________________________________________________________
Placental Insufficiency
May result from
- Umbilical-placental vascular anomalies
- Multiple gestation
- Placental thrombosis, infection, infaction, abruption
- Placentral previa (at lower segment of uterus, cover cervix)
- Cigarette smoking
- inhibit amino acid transport across the placenta
Compromises nutrient transport and may cause intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR)
_____________________________________________________________________
Gestational trophoblastic diseases
Constitutes a spectrum of tumours & tumour-like conditions, characterised by proliferation of pregnancy-associated trophoblast tissue of progressive malignant potential.
There are 3 types:
- Hydatidiform mole (complete mole)
- normal karyotype (46 XX/XY)
- all villi oedematous
- diffuse, circumferential trophoblast proliferation
- elevated hCG
- Absent foetal parts
- 2% choriocarcinoma
- Rapid uterine enlargement
- abnormal uterine bleeding in early pregnancy
- passage of thin, watery fluid & bits of tissue
- diagnosis by ultrasound
- treatment:
- mole removed by curettage
- hysterectomy
- Partial mole
- Karyotype triploid (69 XXY/XXX)
- Some villi oedematous
- focal slight trophoblast proliferation
- less elevated hCG
- foetal parts present
- choriocarcinoma rare
- Invasive mole
- mole penetrates & perforate the uterine wall
- invasion of myometrium by hydropic chorionic villi
- proliferation of cytotrophoblast & syncytiotrophoblast
- hydropic may embolise to distant sites (but dont grow)
- benign
- rupture of uterus –> hemorrhage
- Choriocarcinoma
- epithelial malignant neoplasm of trophoblastic cell
- from pregnancy/abortion
- No chorionic villi
- Abnormal proliferation of cytotrophoblast & syncytiotrophoblast
- Invade myometrium
- penetrate blood vessels & lymphatics
- hemorrhage, ischaemic necrosis
- metastasize
- Clincal features:
- irregular spotting of bloody brown
- foul smelling fluid in the course of pregnancy, abortion or curettage
- hCG elevated (higher than moles)
- Gestational choriocarcinoma has better prognosis
- non gestational choriocarcinoma more resistant to therapy