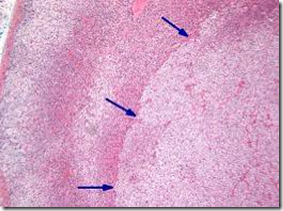
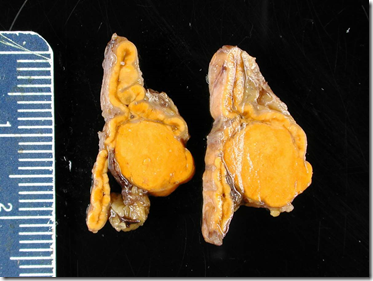
OSPE: Refer histoloy of adrenal gland to identify the zones.
TUMOURS OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX
- Adenoma
- Adenocarcinoma (malignant)
- Rare
- Hormonal symptoms (depending on the hormone hypersecretion)
- Virilization
- Hyperaldosteronism, Cushing’s
- Association with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder)
- Carney complex (autosomal dominant)
CT scan. White: bone
MRI. Bone is not white.
_____________________________________________________________
Adrenal Cortical Adenoma
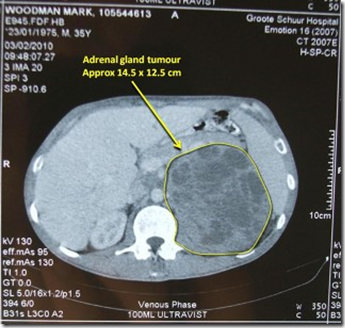
- ‘Incidentalomas’ – incidental finding in 4% of patient’s imaging.
- Most common: primary hyperaldosteronism
Clinical features:
- Depends on hormonal secretory status
- Retroperitoneum structure: more space, less mass effect (more hormonal effect)
- Most common: Aldosterone producing CONN’s syndrome
- Follower by – > Cushing’s & virilization.
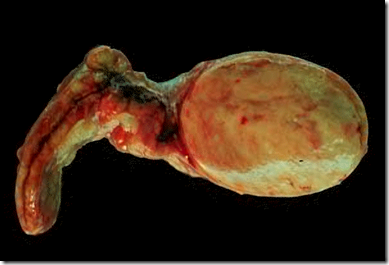
Macroscopic:
- well-circumscribed
- intra-adrenal (inside adrenal gland)
- ‘testical’ appearance
- rarely haemorrhagic/necrotic
- aldosterone-secreting: bright yellow
- Cushing’s: yellow –> tan
- Lipofuscin deposition: black adenoma
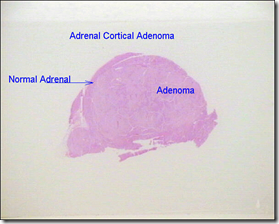
Microscopic:
- well-circumscribed
- recapitulates the cells of the adrenal cortex
- clear cells with abundant intracytoplasmic lipid (zona fasciculata)
- compact cells (zona glomerulosa)
- intermediate cells
- adjacent adrenal cortex: suppressed/atrophy
- when treated: presence of spironolactone bodies
CONN’s Syndrome (hyperaldosteronism)
- Hypertension (mild to moderate)
- Hypokalemia (episodic) –> muscle weakness, cramping, arrhythmia
- Headaches
- Polydipsia, polyuria (not diagnostic)
Blood test done during episode.
- Rarely caused by adrenal cortical carcinoma
- Adenoma on CT not always Conn’s
- Conn’s may be due to small nodules on CT
Therefore a blood test will be more diagnostic than CT.
Cushing’s
Cushing’s syndrome: disorder caused by high levels of cortisol
Cushing’s disease: disorder caused by high levels of ACTH secretion by pituitary gland.
_____________________________________________________________
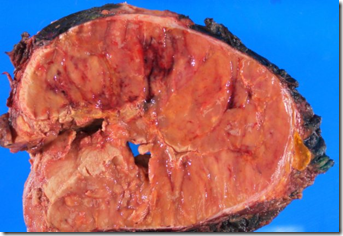
Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma
- 3% of all endocrine neoplasm
- more in females
Investigation:
- CT scan
- MRI
- PET scan
Tumour usually quite large – more than 5cm.
- Recapitulate normal endocrine cortex
- Patternless
- Degenerative changes (hemorrhage, necrosis)
- Mitoses
- Nuclear atypia
- Invasion of capsure & large veins
Criteria for malignancy:
- Tumour size – more than 5cm
- Mitotic rate – more than 2/10 high power field
- Presence of capsular/vascular invasion
- MIB1/Ki-67 labelling index – 5-20%
- NO STAGING SYSTEM (because rare)