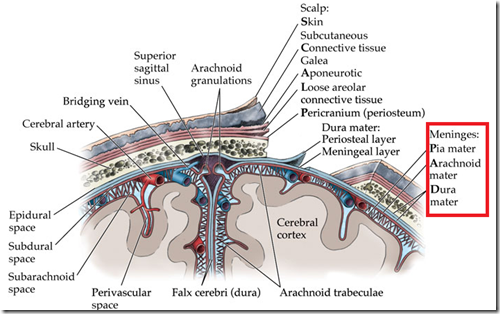
Meninges
- Dura mater
- outer layer lining the skull
- Arachnoid mater
- Space beneath is the subarachnoid space
- contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- contains blood vessels
- Pia mater
- covers the brain
_____________________________________________________________
Subarachnoid space
- Space between the arachnoid and pia mater
- contains CSF
- Lies over the hemispheres
- the space is narrow
- At the cerebello-medullary angle
- pia mater and arachnoid mater widely separated
- At certain parts of the base of the brain, the arachnoid is separated from the pia mater by wide intervals, which communicate freely with each other
- Cerebromedullary cistern
- Meninges covering the brain is continuous with the spinal cord
- through the foramen magnum
- Subarachnoid space around the brain continuous with spinal cord
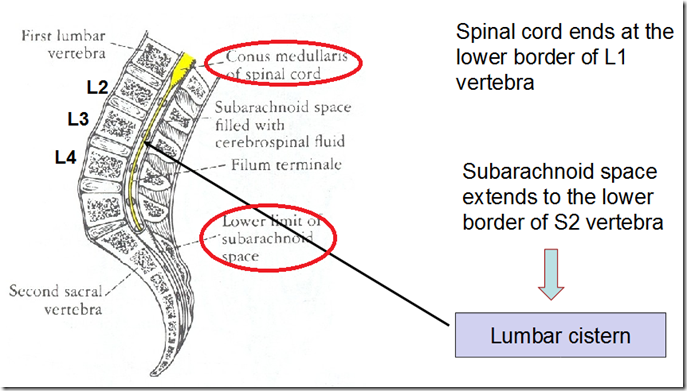
- The spinal cord ends at
- lower border of L1 vertebrae
- Subarachnoid space extends to
- lower border of S2 vertebrae
- Lumbar cistern
- a subarachnoid space in the spinal cord, where the dura mater ends, filled with cerebrospinal fluid
- enlargement of the subarachnoid space between the conus medullaris of spinal cord (about vertebral level L2) and inferior end of subarachnoid space and dura mater (about vertebral level S2); occupied by the posterior and anterior roots constituting the cauda equina, the terminal filum, and cerebrospinal fluid
- are where lumbar puncture is done
- between L2-L3 or L3-L4 levels
- so that won’t cause damage to the spinal cord
- Arachnoid granulations/Arachnoid villi
- are prolongations of arachnoid mater
- forming a tuft through the dura mater
- into the superior sagittal sinus
- Function:
- transfers CSF from subarachnoid space into the venous system
_____________________________________________________________________
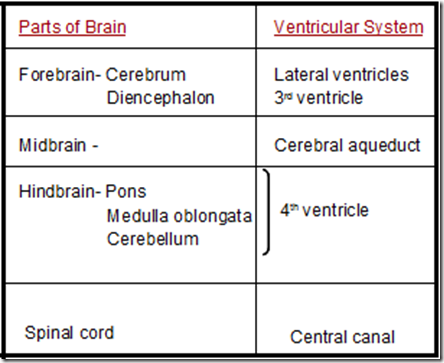
Ventricles of the brain
- Lateral ventricles
- 2 ependymal (thin epithelial membrane) lined cavities
- of cerebral hemispheres
- Consists of
- Anterior horn
- Body
- Posterior horn
- Inferior horn
- Each lateral ventricles connected to 3rd ventricles by
- Interventricular foramen (of Monro)
- 3rd ventricles
- a slit like cavity separating the diencephalon into 2 equal parts
- 4th ventricles
- tent shaped space between
- pons & medulla – INFRONT
- cerebellum – BEHIND
- 2 roofs
- ventral
- dorsal
- Communicates with
- median aperture
- foramen of Magendie
- drains CSF from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna/cerebromedullary cistern
- back into subarachnoid space
- lateral apertures
- foramen of Lushka
- drains CSF from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna/cerebromedullary cistern
- back into subarachnoid space
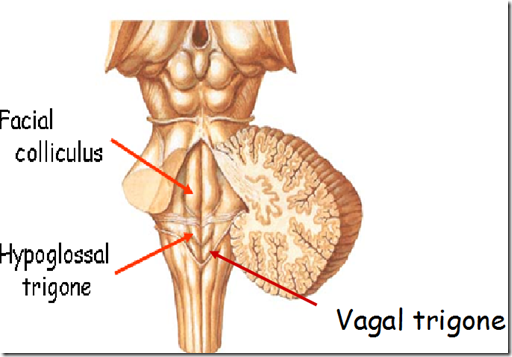
- Floor of the 4th ventricle
- Facial colliculus
- facial nerve fibres looping around the abducent nucleus
- Hypoglossal trigone
- hypoglossal nucleus
- Vagal trigone
- vagus nucleus
_____________________________________________________________________
Cerebrospinal fluid
- Total volume circulation at a time
- 130 ml
- Formation of CSF
- 80% from choroid plexus
- located in the lateral, 3rd & 4th ventricles
- The rest from the ependymal cells
- lining the ventricles
- Rate of production
- 0.5ml per min
- Pressure measured in the lumbar cistern
- in recumbent position
- 70 – 150 mm H20
- Composition of CSF
- clear and colourless liquid
- glucose 1/2 of that in blood
- 50-85 mg/100ml
- Protein
- 15 – 30 mg/100ml
- Cells
- 1-3 cells / Cu mm
- (lymphocytes)
- Functions
- Protects CNS from trauma
- Buoyancy of CSF reduces the concussion damage to the brain when the cranium moves suddenly
- Nourishes the brain
- Removes metabolites from CNS
- Carries pineal secretions to pituitary gland
- CSF secretion
- Choroid plexus
- vascular pia projecting into ventricles as a fringe covered with ependymal covering
- the area on the ventricles of the brain where CSF is produced by modified ependymal cells
- secretes major part of the CSF
- Present in all components of the ventricular system (except cerebral aqueduct, occipital & frontal horn of lateral ventricles)
- Body & inferior horn (of lateral ventricles)
- Roof of (3rd ventricle)
- Inferior part of (4th ventricle)
- Tela choroidea
- 2 layers of pia with high vascular plexus
- in between coming into contact with the ependymal layer of the ventricles
- CSF circulation
- within the ventricles
- by ciliary action of the ependymal cells
- within the subarachnoid space
- by the pulsation of the arteries on the surface of brain & spinal cord
- CSF absorption
- When the CSF pressure exceeds venous sinus pressure
- CSF seeps through channels in arachnoid villli (arachnoid granulations) into venous sinus
- If venous sinus pressure higher that CSF pressure
- tips of the villi are compressed
- so that the channels are closed
- prevents reflux of blood into CSF