Incomplete notes. For more info, read up David Chong’s lecture.
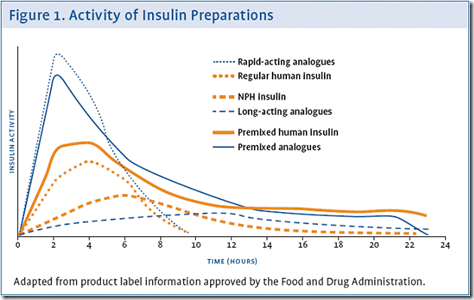
Insulin types
Older types
- Soluble
- quick onset
- short duration
- NPH, ‘Lente’ & biphasic
- intermediate onset
- intermediate duration
- ‘Ultralente’
- slow onset
- long duration
Newer types (recombinant analogues)
- Lispro Aspart Glulisine
- slow onset
- long duration
- Mimics pulsed secretion (give with meals)
- Glargine Detemir
- long duration
- Mimics basal secretion (give during bedtime)
Unwanted effects of insulin
- Hypoglycemia
- didnt eat / too large dose
- lightheadedness
- tachycardia, sweatiness
- skeletal muscle tremor
- loss of consciousness, seizures
- give glucose + glucagon
- Insulin allergy
- IgE antibodies to non-insulin protein contaminants
- rare now, because now follow highly purified insulin preparations
- True insulin resistance
- IgG mediated
- Hypertrophic Lipodystrophy
- hypertrophy of subcutaneous fatty tissues at injection sites
- avoid by using different injection sites
Insulin pump
____________________________________________________________________
Treatment strategies
Enhance incretin effects
- GLP-1 analogues
- Liraglutide
- longer half life
- Exenatide
- Mechanism of action:
- glucose dependent insulinotropic effect & reduction in glucagon secretion.
- improves beta-cell function.
- reduces rate of gastric emptying and promote early satiety –> weight loss
- mild nausea,
- transient hypoglycemia inhibitors
- DPP-4 inhibitors/’Gliptins’
- Reduces HbA1c
- Mild hypoglycemia
- No effect on satiety & gastric emptying –> weight neutral
- No effect on beta-cell function
Enhance insulin secretion (using secretagogues)
- Sulphonylureas
- mimics glucose stimulated insulin secretion
- 1st generation obsolete
- 2nd generation (gliclazide)
- care in the elderly
- dose dependent hypoglycemia
- care in renal impairment if serum cretinine is high
- eventual treatment failure due to complete loss of beta-cell function
- extra pancreatic effects
- Meglitinides
- similar to above
- modulate K+ channel closing
- quicker action & shorter duration than sulphonylureas
- effective if taken after meals
- adverse effect: hypoglycaemia
Enhance insulin action/sensitivity
- Metformin (biguanide)
- important for type 2 diabetes
- stimulate tissue glycolysis
- reduces hepatic & renal gluconeogenesis
- slows GI glucose absorption
- Reduces glucagon levels
- Indications:
- overweight patients (Can lose weight)
- type 2 diabetes on insulin (lower futher HbA1c)
- UKPDS lowers mortality
- Adverse effects
- Abdominal discomfort, nausea, diarrhea
- severe lactic acidosis
- Will not cause hypoglycemia
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDD)
- Nuclear Peroxisome Proliferator- Activated Receptors (PPAR)
- activate transcription of genes affecting glucose & lipid metabolism
- adipocyte differentiation
- Binds to PPAR-gamma
- Pioglitazone & rosiglitazone
- Effects:
- increase tissue sensitivity to insulin
- lowers glucose, FA and TG
- Decreases HbA1c)
- Adverse effects
- Weight increase
- Redistribution of fat
- Fluid retention
- Rosiglitazone
- increases risk of heart failure
- idiosyncratic hepatic failure
Reduce glucose absorption
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (Acarbose & Miglitol)
- Inhibit glycoside hydrozylase (carbohydrate digesting enzymes)
- suitable for prevention in prediabetes
- Taken with meals
- Adverse effects:
- more undigested carbohydrate available to colonic flora
- flatulence
- diarrhea
Replace islet cells/transplantation
_____________________________________________________________
Summary
Mnemonic: GMT S MR AD
For glycaemic control
- alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
- lowers HbA1c more than the others
For better lipid profile
- Metformin
- lowers LDL
- Thiazolidinediones (TZD)
- raise HDL & LDL
For weight loss
- Metformin
- GLP-1
Causes weight gain
- Sulphonylureas
- Metiglinides
- TZD
Weight neutral
- DPP-4
Enters hypoglycemia
- Sulphonylureas
- repalinide
Adverse effects
- Metformin
- lactic acidosis
- GI upset
- TZD
- risk of heart failure (Rosiglitazone)
_____________________________________________________________________
Extras:
Anti-obesity agents
- Orlistat
- inhibit intestinal lipases
- fat remains in gut –> steatorrhoea & fecal incontinence
- Sibutramine
- enhances satiety
- raises BP & heart rate –> hypertension
Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Hyperglycemia (HONK)
- Severe hyperglycemia without ketosis
- In type 2 diabetes
- Absense of ketosis because enough insulin secretion to inhibit ketogenesis
- Mortality high in elderly
- plasma osmolality high
- dehydration
- depressed consciousness
- risk of arterial thrombosis
- Treatment
- adjust osmolality
- fluid replacement
- carefull insulin use
- sensitive to insulin action
- anticoagulant