Read from Dr. Sheila Rani’s notes!
Normal menstruation
- normal volume
- 30ml – 80ml
- interval between cycles
- 28 days
- duration of flow
- 2-7 days
Amenorrhea
- absence of menstruation in excess of 6 months
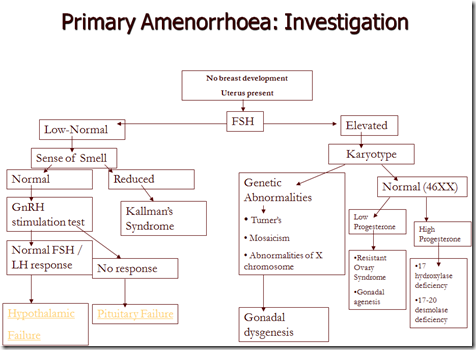
Primary:
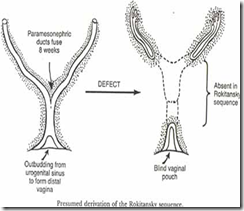
Rokitansky’s syndrome
- no onset of menstruation by age 16 with normal sexual development
- no onset of menstruation by age with no normal sexual development
- Causes: Outflow tract
- imperforate hymen/vaginal atresia
- hypoplasia of vagina
- testicular feminisation
- Mayor-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (Mullerian Agenesis)
- Causes: Ovary
- Turner’s syndrome
- Ovarian agenesis (failure of development)
- Resistant ovary syndrome
- Increase in FSH
- Premature menopause
- Causes: Hypothalamo-pituitary axis
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Anorexia nervosa
- Kallman’s syndrome
- hypogonadism
- Hypothyroidism
Secondary
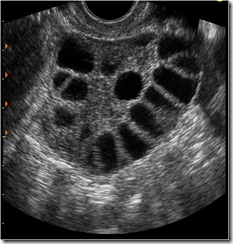
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Asherman’s syndrome
- Absense of maturation in excess of 6 months in a previously menstruation woman
- 6 months if cycles were regular
- 12 months if cycles were irregular
- Causes
- pregnency, menopause, anovulation
- premature ovarian failure
- hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction
- hyperprolactinemia
- Polycycstic ovarian syndrome
- recurrent miscarriages
- hyperandrogenism
- high LH
- weight gain
- Androgen producing tumour
- Asherman’s syndrome
- Thyroid dysfunction
- Hemochromatosis
- Drug induced
- drugs that increase prolactin
- cimetidine
- metoclopramide
- methyldopa
- haloperidol
- drugs that induce menopausal state
- GnRH analog
- Danazol
- Contraceptive agents
- progestogens (Depo, implant)
- Post-pill
Oligomenorrhea
- reduction in frequency of menstruation (6 weeks-6 months)
- more than 6 months: amenorrhea
- low oestrogen level
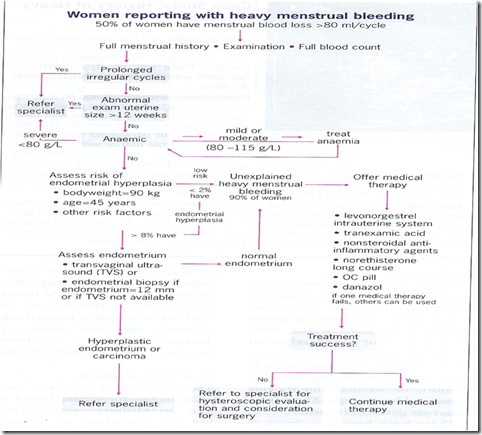
Menorrhagia
- menstrual blood loss of 80ml or more
- Causes
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)
- loss of coordinated cyclic hormonal changes
- age determinates
- 20 yo
- secondary to anovulation
- 20-40 yo
- PID, IUCD, OCP
- Adenomyosis
- Endometriosis
- Tryroid disease
- >40 yo
- Anovulation
- rule out neoplasia
- no organic cause
- Organic pelvic lesions (benign/malignant)
- leiomyomas
- endometriosis/adenomyosis
- endometrial polyps
- endometrial hyperplasia
- infections (PID, TB)
- Intrauterine contraceptive device
- Extragenital problems
- coagulopathies, endocrinopathies, iatrogenic
- Pregnancy complications
- Age dependent causes
- prepubertal DUB
- perimenarchal DUB
- lack of development of HPO axis
- absense of regular LH
- Continued unopposed oestrogens
- reproductive
- post menopausal
- diminished no. of follicles in ovary
- FSH high
- Circulating estradiols low
- fail to ovulate, corpus luteum function fails
- unopposed oestrogen
Atrophy of endometrium
- total absence of oestrogen/ failure of uterine receptors to become responsive to oestrogen
- postmenopausal
- rupture of dilated capillaries beneath atrophic surface epithelium
Dysmenorrhea
- pain during menstruation
Investigations
- Haematology
- Hb, platelet count, PT, APTT, bleeding time
- Thyroid functions: TSH, T3, T4
- Diagnostic tests
- uterine curettage (D&C)
- hysteroscopy
- Ultrasound
- Laparoscopy
Treatment
- Medical
- Surgical
- Endometrial curretage
- Endometrial ablation
- Hysterectomy