General features of the ear

3 parts of the ear:
- External ear
- involved in hearing
- Anatomy:
- auricle: funnel shaped, elastic cartillage
- 3 parts:
- helix
- concha
- lobule
- 3 parts:
- external auditory meatus
- 2.5cm curved tube
- Outer 1/3: cartilage
- Inner 2/3: Bony (temporal bone)
- Modified sweat glands –> secrete cerumen
- prevents drying
- protects from insects
- Blood supply
- posterior artery
- auricular a.
- superficial a.
- temporal a.
- Sensory nerve
- Auriculo-temporal
- branch of V3
- Great auricular
- C2, C3
- Lesser occipital
- C2
- Auricular branch of 10th CN
- Vagus
- Auriculo-temporal
- auricle: funnel shaped, elastic cartillage
- Middle ear
- involved in hearing
- Internal ear
- involved in hearing & equilibrium
Hearing & Balance
Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
- Thin connective tissue membrane
- vibrates in response to sound
- Transfers sound energy to middle ear ossicles
- Boundary between outer & middle ear
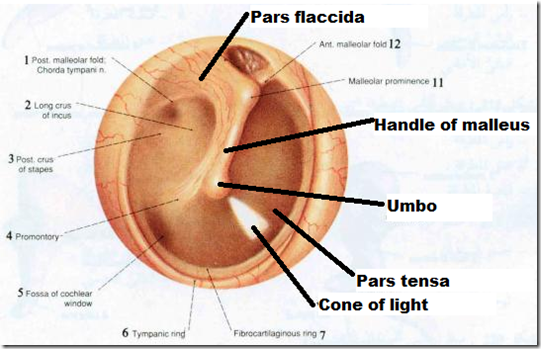
- Anatomy:
- pearly gray membrane
- oblique
- facing – towards floor
- downward
- forward
- lateral
- Layers
- Outer: Skin
- Middle: Fibrous tissue
- circular & radial fibres maintain elastic tension
- helps to multiply magnitude of sound wave
- circular & radial fibres maintain elastic tension
- Inner: Mucous membrane
- Lateral part
- concave
- depression: umbo
- cone of light
- part of tympanic membrane that can be seen
- anterior inferior part
- 2 parts
- pars flaccida
- pars tensa
- Nerve supply:
- External surface
- auriculo-temporal nerve
- vagus nerve (vomiting)
- Internal surface
- glossopharyngeal nerve
- External surface
- Very sensitive
- if got perforation, be careful of damaging chorda tympani nerve
- facial nerve
- running along tympanic membrane & supply the tongue (taste)
- if got perforation, be careful of damaging chorda tympani nerve
_____________________________________________________________________
Middle ear (tympanic cavity)

- A small, air-filled mucosa-lined cavity
- flanked laterally by the eardrum
- flanked medially by the oval & round window
- Epitympanic recess
- superior portion of the middle ear
- Pharyngptympanic (Eustachian) tube
- connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
- equalizes pressure in the middle ear cavity with the external air pressure
- in the floor (tympanic plate)
- has internal jugular vein
- if fracture, can cause severe bleeding
- Boundaries
- Superior face
- paper thin plate of bone (Tegmen tympani/tegmental wall)
- separates the cavity from cranium and the meningeal coverings of the brain
- has implications regarding pathways for infection
- paper thin plate of bone (Tegmen tympani/tegmental wall)
- Inferior face
- Tympanic plate of temporal bone
- spearates the cavity from the jugular fossa
- large groove that accomodates the internal jugular vein
- spearates the cavity from the jugular fossa
- Tympanic plate of temporal bone
- Lateral wall
- tympanic membrane
- above it: epitympanic recess
- tympanic membrane
- Medial wall
- cochlea/inner ear
- important landmarks
- oval window
- a kidney shaped opening into the vestibule of the inner ear
- occupied by the footplate of the stapes
- are of tympanic membrane is 17x the oval window.
- as the area increases, pressure increases
- amplitude of sound wave increased at oval window
- round window
- a circular opening into the basal turn of the cochlea which is covered by a thin membrane
- promontary
- a rounded prominence caused by the 1st turn of the bony labyrinth of the inner ear
- oval window
- Anterior wall
- carotid wall
- internal carotid artery runs behind this wall
- major auditory landmark
- eustachian tube
- above it: bony canal for tensor tympani
- malleous, incus &
stapes- transmit vibratory motion of the eardrum to the oval window
- move as a unit
- inertia is small, so once sound vibrations have ceased, the vibrations of the ossicles also terminate abruptly (bcos of the ligaments)
- the 2 media crossed by sound: air & cochlear fluid
- the more different the characteristics of the 2 media, the more sound energy will be reflected at the boundary
- acoustic resistance of cochlear fluid MORE than air
- dampened by the tensor tympani & stapedius muscle
- transmit vibratory motion of the eardrum to the oval window
- eustachian tube
- carotid wall
- Posterior wall
- mastoid wall
- landmarks
- aditus to mastoid antrum
- entrance to mastoid antrum –> mastoid air cells
- pyramidal eminence contains stapedius muscle
- canal for facial nerve
- chorda tympani nerve
- aditus to mastoid antrum
- Superior face
Sound transmission -factors
1) Difference between air and cochlear fluid
- transmission
2) Difference between area of tympanic membrane & oval window
- increased amplitude of sound at oval window
Acoustic reflex
- In response to loud sounds (80-90 dB above)
- contraction of tympanic muscles as a reflex (smallest striated muscles in the body)
- tensor tympani
- stapedius
- ossicles become more stiff, and less force is delivered to the cochlea
- contraction of tympanic muscles as a reflex (smallest striated muscles in the body)
| Very quiet (whisper) | 30 dB |
| Quiet (radio) | 40 dB |
| Moderate (vacuum cleaner) | 70 dB |
| Very noisy (alarm clock) | 80 dB |
| Possible hearing loss | 90 dB or more |
Eustachian Tube
- Orientation
- downward
- forward
- medially
- Parts
- Osseous portion
- begins in the anterior wall of the middle ear cavity
- Cartilaginous portion
- most of the tube is cartilaginous
- Isthmus
- where the 2 portions meet
- Osseous portion
- Tensor palatini muscle
- opens blocked tube
- by yawning or swallowing
Cochlea
- spinal, conical, body chamber
- extends from the anterior vestibule
- divided into 3 chambers
- Scala vestibuli
- filled with perilymph
- Scala media
- filled with endolymph
- Scala tympani
- terminates at the round window
- filled with perilymph
- Scala vestibuli
- Similarities between Scala vestibuli & scala tympani
- filled with perilymph
- basilar membrane supports the organ of Corti
- contains hearing receptor
- cochlear branch of 8th nerve runs from the organ of Corti to the brain
Q: What is the sensory apparatus of the ear?
A: Organ of Corti (type of neuron: bipolar neuron)
Route of sound transmission
- Outer ear
- pinna
- auditory canal
- eardrum
- Middle ear
- malleous
- incus
- stapes
- -> to oval window
- Inner ear
- scala vestibuli & scala tympani
- -> to cochlear duct
- sound waves penetrate thru cochlear duct
- vibrate the basilar membrane
- stimulation of organ of corti
- -> excite specific hair cells according to frequency of sound
- Bending cilia (generate AP)
- opens mechanically-gated ion channels
- causes a graded potential
- release of a neurotransmitter (probably glutamate)
- neurotransmitter causes cochlear nerve to transmit impulses to the brain
- where sound is perceived
_____________________________________________________________________
Structural abnormalities (conductive deafness)
- earwax (impacted)
- eardrum perforation/inflammation
- autosomal disorder (sclerosis of ossicles)
Sensory deafness
- cochlear nerve damage
Physical examination
- Weber test
- test for lateralization
- press the tuning fork on the top of patient’s head in the midline and ask if patient hear the sound
- normally,
- sound is head in the center of head/equally in both ears
- Conductive hearing loss
- vibration louder louder on the side of the conductive hearing loss
- Rinne test
- compares air conduction to bone conduction
- place the tuning fork (512 hz) on the mastoid eminence firmly & tell patient to say ‘now’ when they can no longer hear the vibration
- remove the tuning fork and place it near the ear (without touching), compare the sound
- Normally,
- greater air conduction than bone conduction, therefore can hear the vibration longer with the fork in the air.
- sound is equal on both sides
- If air conduction more than bone conduction (usually normal)
- sensorineuronal deafness/hearing loss
- right sided deafness, left side louder
- sensorineuronal deafness/hearing loss
- If bone conduction more than air conduction (cannot hear the vibration via air conduction)
- conductive deafness/hearing loss
Referred pa
in to ear
- from the 5th, 7th, 9th, 10th cranial nerves
- TMJ
- Tonsils –> vagus nerve –> external ear
- Throat
- Eustachian tube
- Teeth –> inf & sup alveolus (V2, V3)
- Tongue
Otitis media
- From obstruction of Nasopharynx
- adenoid hypertrophy
- tumours
- cleft palate
- Obstruction of auditory tube
- due to infection/allergy
- metaplasia of epithelium – chronic infection
- Complications
- acute mastoiditis
- facial nerve paralysis
- acute labyrinthitis
- sigmoid sinus thrombophlebitis
- CNS infection
Otosclerosis
- A primary bone dyscrasia
- abnormal bone growth near the middle ear
- Involvement of temporal bones
- autosomal dominant
- Involvement of oval window
- footplate fixation & persistent conductive hearing loss
- Involvement of cochlear endosteum
- produce sensorineuronal hearing loss
- thickened bone causes vibration of perilymph to become less
- produce sensorineuronal hearing loss