*Read from written notes before reading from this post

- Psoas major
- origin:
- transverse process of lumbar vertebrae
- intervertebral disc
- Insertion
- pass behind inguinal ligament
- Iliopsoas tendon inserted into lesser trochanter of femur
- Action
- flexes thigh on trunk at hip joint
- flexes trunk on thigh
- Nerve supply
- L2, L3 roots

Quadriceps

- Adductor magnus
- pubic part
- obturator nerve

- Ischial part: Hamstring
- Nerve supply:
- tibial part of sciatic nerve
- Arise from ischial tuberosity
- inserts below knee (exception adductor magnus)
- Action
- flexion of knee
- extension of hip

- Gluteus maximus
- Action
- extensor of hip
- lateral rotator of hip
- Maintain knee in extended position
- via ilio-tibial tract
- Nerve supply
- inferior gluteal nerve
- Gluteus medius & minimus
- Action
- Abduction of hip
- medial rotation of hip
- Stabilizes pelvis
- do not allow tilt downwards when foot of opposite side is off the ground
- If fall on left side, then tredelenburg +ve (on right side)
- abductor muscles dysfunction on opposite side

Tredelenburg +ve
Layers of the foot
- 1st layer
- abductor hallucis
- flexor digitorum brevis
- abductor digitorum minimus
- 2nd layer
- tendons of flexor digitorum longus
- flexor hallucis longus
- lubricals (same action as in upper limb)
- flexes metatarsophalangeal
- extends interphalangeal joints
- Quadratus planae
- 3rd layer
- Flexor hallucis brevis
- Adductor hallucis
- Flexor digitorum brevis
- 4th layer
- Plantar interossei (3 in total)
- Dorsal interossei (4 in total)
- Tendon of tibialis posterior (medial side)
- Peroneus longus (lateral side)
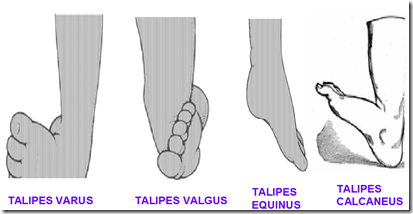
Abnormalities of the foot
- Talipes varus
- inverted
- Talipes valgus
- everted
- Talipes equinus
- plantarflex
- Talipes calcaneus
- dorsiflex
- Talipes equinovarus
- most common
- club foot
- plantarflex + inverted
- like walking on their ankles
_____________________________________________________________________
Question
- The gluteus maximus muscle is
- Supplied by superior gluteal nerve F
- Is said to be homologous with deltoid in the upper limb
- Is one of the group of 6 lateral rotators of the hip joint T
- Acts through the iliotibial tract to prevent full extension of the knee joint F (hip joint)
- Is an abductor of the hip active during the stance phase of locomotion F (extension of hip)
- A 19 y/o teenager was dancing in clogs in an ethnic street festival when she inverted her left foot. She presents to your office the next day with a swollen foot, but mainly complains about tenderness on the lateral aspect of the foot along the plantar surface. You carefully palpate her foot and determine that she has tenderness over the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal bone. What muscle has avulsed from its insertion onto the tuberosity of the 5th metatarsal?
- Abductor digiti minimi CORRECT
- Fibularis (peroneus) brevis
- Fibularis (peroneus) longus
- Tibialis anterior
- Tibialis posterior
_____________________________________________________________________
Knee jerk – femoral nerve (L3, L4)
Common injury of sacral plexus
- Common peroneal nerve
- Damages
- loss of dorsiflexion
- loss of eversion
- sensory loss (over lower leg & dorsum)
- Presentation
- foot in plantarflexion, inverted & adducted
- Sciatic nerve
- Compression
- lower back pain (sciatica)
- abnormal gait
- Spinal root affected: L4 – S4
- Deep peroneal nerve
- Foot drop
Diagnosis
- Tinel’s sign
- is a way to detect irritated nerves. It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins & needles" in the distribution of the nerve

Thanks 4 the information it’s a great relieve. I will like to recieve updates on lower limb anatomy expecially “applied anatomy”
Thank.