Note: Important for OSPE & read up foundation 1!
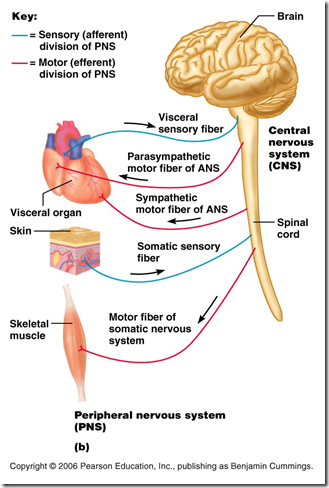
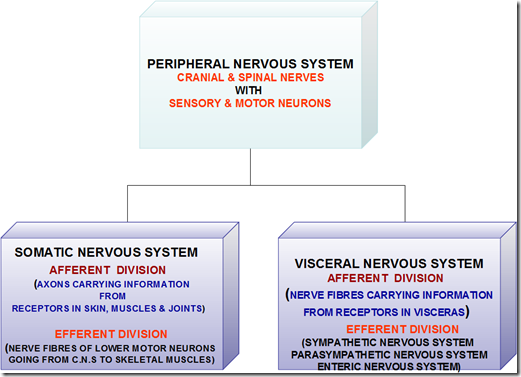
Peripheral nervous system
- Made up of
- nerve cell bodies
- nerve fibres
- cranial nerves
- spinal nerves
- Connects
- CNS with peripheral structure
- Function
- afferent (sensory) neuron
- carry impulse from sensory receptors to CNS
- efferent (motor) neuron
- carry information from CNS to muscles/glands
- Accessory nerve
- 2 parts
- cranial part
- spinal part
- arise from C5, C6
- Injury is possible
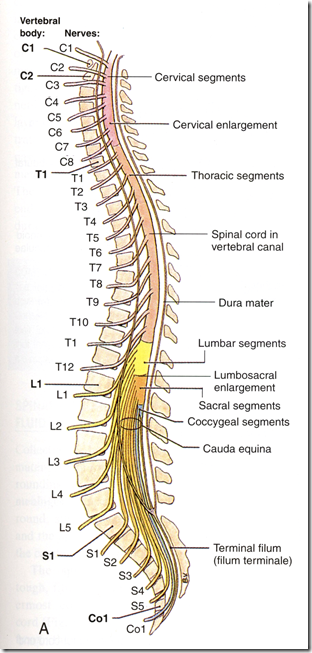
Spinal cord
- It is the major reflex centre & conduction pathway
- Length: 45 cm
- Extent:
- from foramen magnum
- to lower border of L1
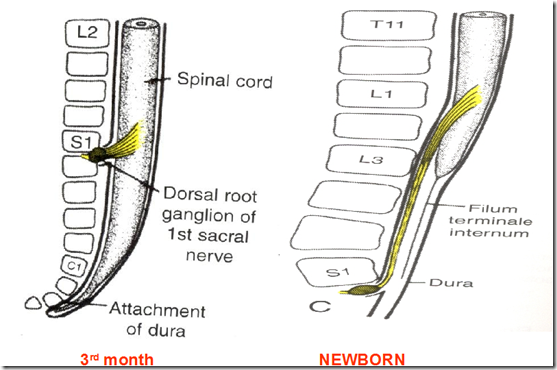
- newborn: upper border of L3
- 2 enlargements
- cervical
- lumbar
- Midline demarcation
- anterior median fissure
- posterior median sulcus
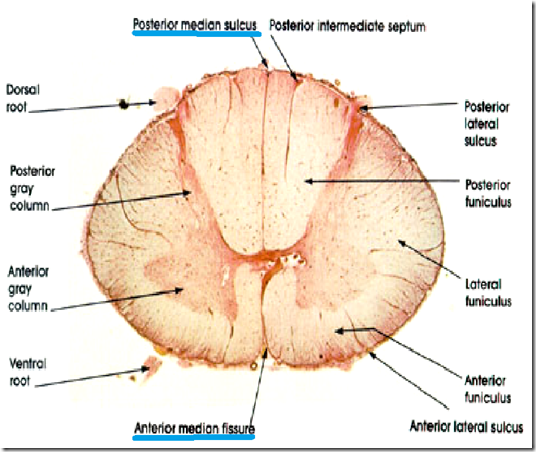
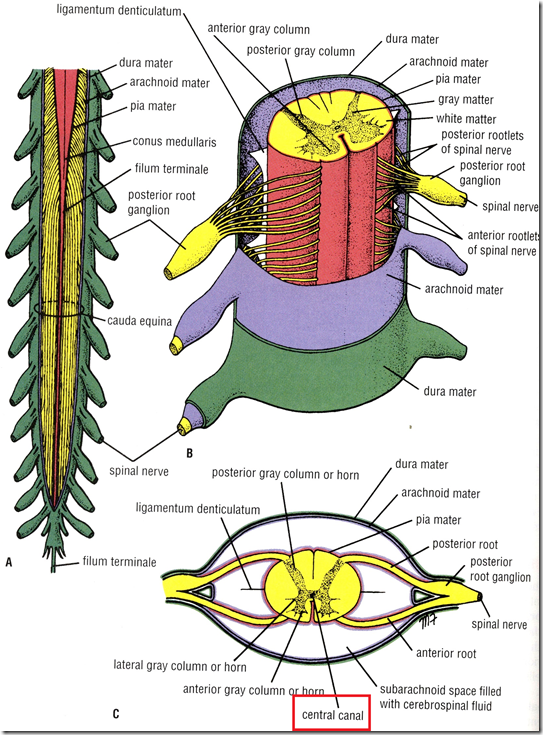
- Cross section
- Gray mater
- anterior gray column
- posterior gray column
- gray commissure (central canal)
- lateral gray column
- T1 – L2
- S2,3,4
- White mater
- anterior funiculus
- lateral funiculus
- posterior funiculus
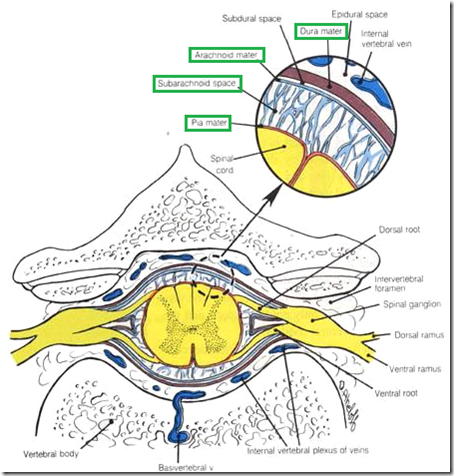
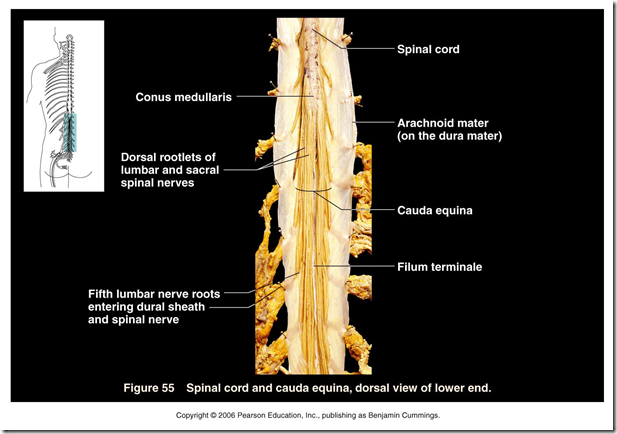
- Spinal meninges
- Dura mater
- dense, fibrous
- from foramen magnum –> S2
- above it epidural space
- below it subdural space (negligible)
- Arachnoid mater
- delicate, impermeable
- from foramen magnum –> S2
- Subarachnoid space
- cerebrospinal fluid here
- Pia mater
- fine, vascular
- from foramen magnum –> coccyx
- as filum terminale
- thickened on either side of nerve roots
- pairs of ligamentum denticulatum
- Denticulate ligament
- attached to pia mater
- actually pia mater extension
- helps in fixation of spinal cord
- Cauda equina
- bundle of lumbar & sacral nerve roots
- in the subarachnoid space
- caudal to termination of spinal cord
- looks like horse tails
- Conus medullaris
- ending of spinal cord
- lower tapering of spinal cord
- at lower border of L1
- from L2 – coccyx
- just spinal nerve roots
- extensions
- Filum terminate
- condensation of pia mater
- from lower end of spinal cord to coccyx
- attached to sacral
- fixation
Spinal column
- circular part of spinal cord
- Rootlets of 1 spinal nerve emerge
- 31 spinal segments – corresponding to spinal nerves
- 8 cervical
- 12 thoracic
- 5 lumbar
- 5 sacral
- 1 coccygeal
Blood supply
- Anterior spinal artery
- from vertebral artery
- supply anterior 2/3 of spinal cord
- Posterior spinal artery
- from posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- supply posterior 1/3 of spinal cord
- Radicular arteries
- reinforce the anterior & posterior spinal artery
- enter via intervertebral foramina
- from
- deep cervical artery
- intercostal artery
- lumbar artery
- running along spinal nerve roots
- mostly supply lower spinal cord
- Arteria Radicularis Magna (Artery of Adamkiewicz)
- major source of blood supply to
- lower 2/3 of spinal cord
- Clinical signs of spinal cord ischaemia
- flaccid
- paraplegia
- both lower limbs paralysed
- areflexia
- Absence of neurologic reflexes
- eg. knee jerk
- loss of pain
- loss of temperature sensation
- autonomic deficits
- atonic bladder
- Spinal cord is short , vertebral column is long
- spinal segment not the same level as vertebrae
| VERTEBRAE | SPINAL SEGMENT | EXAMPLE |
| Cervical vertebrae | Add 1 | C3 vertebrae – C4 spinal segment |
| Upper thoracic (T1 – T6) | Add 2 | T4 vertebrae – T6 spinal segment |
| Lower thoracic (T7 – T9) | Add 3 | T9 vertebrae – T12 spinal segment |
| T10 thoracic | L1 & L2 | |
| T11 thoracic | L3 & L4 | |
| T12 thoracic | L5 | |
| Lumbar 1 | Sacral & coccygeal spinal segment |
- How spinal cord can be affected?
- compression
- metastasis
- Intervertebral disc prolapse
- fracture
- Most common cervical spinal injuries involve C4/C5
- A person who has had a burst fracture of the C5 vertebral body
- injures C6 spinal segment
- wrist extensors weak
- sensation below C6 severely compromised
- injures C4 spinal roots
- exits the spinal column btwn C4 & C5 vertebrae
- loss of sensation in C4 dermatome
- weak deltoids (supplied by C4)
- Dermatome
- area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
- loss of sensation on a certain dermatome
- able to tell which spinal nerve affected
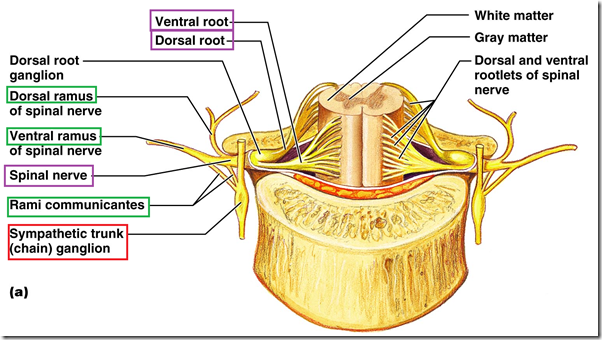
How are spinal nerves formed?
- At each spinal segment
- 1 pair of nerves exit to the left
- 1 pair of nerves exit to the right
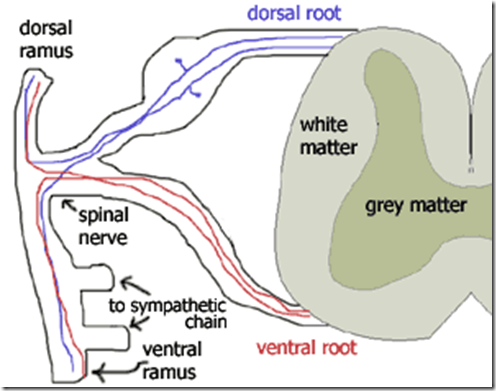
- Dorsal root & ventral root meet
- forming spinal nerve
- Comes out through intervertebral foramina
- Spinal nerve divides into
- Dorsal ramus
- Ventral ramus
- Meningeal ramus
- Rami communicating to sympathetic chain
What are plexuses?
- Ventral rami of spinal nerves interconnect to form several networks of nerves
- Plexuses (5 in total)
- Cervical
- C1 – C4
- Brachial
- C5 – C8, T1
- Lumbar
- L1 – L4
- Sacral
- L4 – L5, S1 – S3
- Coccyx
- S4 – S5, Coccygeal 1
- T2 – T12 do not form plexus
- innervate muscles & skin of thoracic, abdominal wall
- as intercostal nerves
- In a plexus, nerve fibres of different spinal nerves are sorted & recombined
- Peripheral nerves coming out of plexuses are composed of
- fibres from several spinal nerve rami
- eg median nerve made up of
- C5, C6, C7, C8, T1
- Question:
- What are the roots forming the brachial plexus?
- Ventral rami of
- must mention this
- C4 5 6 7 and T1
- Components of a typical spinal nerve
- general somatic afferent
- general somatic efferent
- general visceral afferent
- general visceral efferent
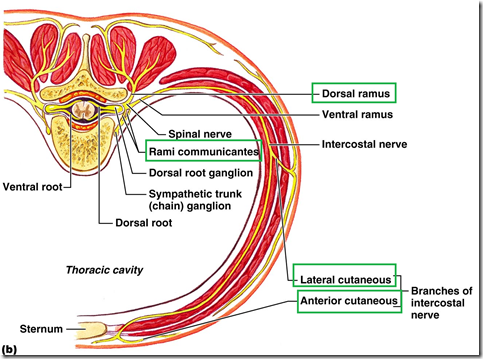
Branches of spinal nerve communicating to sympathetic trunk
- Gray rami communicantes
- White rami communicantes
- Posterior primary ramus
- dorsal cutaneous branch
- muscular branch to erector spinae
- articular to joints of vertebral column
- Anterior primary ramus
- lateral cutaneous branch
- anterior cutaneous branch
- proximal muscular branch
- distal muscular branch
Coverings
- Epineurium
- outer
- Perineurium
- middle
- Endoneurium
- inner
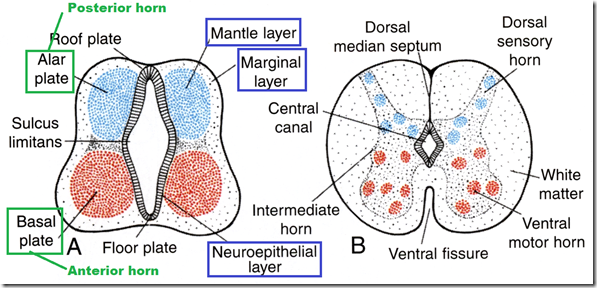
- 3 layers
- neuroepithelial layer
- mantle layer
- marginal layer
- Ventral thickening
- basal plate –> anterior horn cells
- Dorsal thickening
- alar plate –> posterior horn cells
- Boundary (centre)
- sulcus limitans
- Neural crests
- detached from neural tube ectoderm
- forms dorsal root ganglion
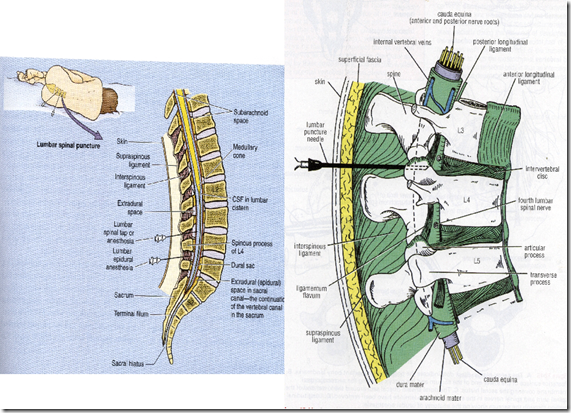
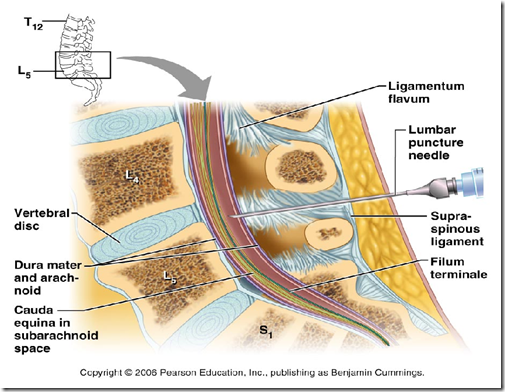
Lumbar puncture
- Between L3 & L4 vertebrae
- Structures pierced
- skin
- thoracolumbar fascia
- interspinous, supraspinous ligament
- ligamentum flavum
- dura mater
- arachnoid mater
- subarachnoid space
http://rch.org.au/clinicalguide/cpg.cfm?doc_id=5178
*lumbar puncture – read up for OSPE
_____________________________________________________________________
Questions
- The following statements concerning meninges of the spinal cord are correc EXCEPT:
- Dura mater is a delicate impermeable membrane F
- Pia mater is a vascular membrane that closely invests the cord T
- Arachnoid mater continues along spinal nerve roots for a short extent T (until S2)
- Dura mater is continuous above through foramen magnum with cranial dura T
- Extradural space contains internal vertebral venous plexus T
- The following statements concerning the arterial supply of the spinal cord are true EXCEPT:
- Posterior spinal arteries supply posterior 3rd of spinal cord T
- Veins communicate with veins of brain and venous sinuses
- Arteria radicularis magna (Artery of Adamkiewicz) arises in the upper thoracic region of from arch of aorta F
- Anterior spinal artery is single but usually arises from vertebral artery T
- Spinal arteries are reinforced by radicular arteries, which are branches of local arteries T
- The following statements concerning the spinal cord are correct EXCEPT:
- Spinal cord has a cervical enlargement for the brachial plexus T
- It possess 34 pairs of spinal nerve F (31 pairs)
- In the adult it ends at lower border of 1st lumbar vertebra T
- Ligamentum denticulatum anchors spinal cord to the dura mater along each side T
- Central canal communicates with the 4th ventricle of brain T
- The following statements concerning CSF are correct EXCEPT:
- Normal pressure is between 60 & 150 mm of water T
- Normal glucose content is 50 to 85 mg per 100 ml T
- It is a clear colorless fluid T
- The cells are polymorphonuclear leucocytes F (mononuclear)
- Compression of internal jugular vein (Queckenstedt sign) can diagnose blockage of subarachnoid space by tumour T










this is awesome! thanks!
You’re welcome!
Learning for the FIPP examination this is very nice , thank you ,