Classification of bones
- Long bones
- bones of the limbs
- Short bones
- carpal
- tarsal
- Flat bones
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Squamous part of temporal
- Irregular bones
- Vertebrae
- hip bones
- Short long bones
- metacarpal
- metatarsal
- Sesamoid bones
- Patella
- Pisiform
- Pneumatic bones
- Maxilla
- Part of frontal air sinus
Skeleton
- Axial skeleton (80)
- skull
- vertebral column
- ribs
- sternum
- Appendicular skeleton (126)
- pectoral girdle
- upper limb bones
- pelvic girdle
- lower limb bones
Microscopic structure of the bone
- Haversian system
- Haversian canal
- Outer circumferential lamellae
- Periosteum
- contains osteoblasts
- endosteum also have osteoblasts
- Interstitial lamellae
- Osteocytes
- Cancellous bone
*Read up from foundation 1
Osteoblasts are at the periphery forming osteocytes.
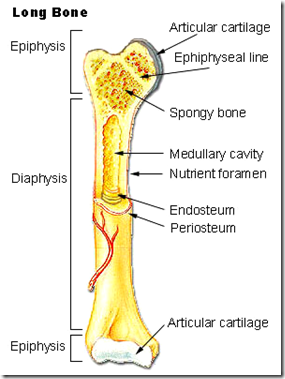
Parts of a growing lone bone
- Epiphysis
- Diaphysis
- Epiphyseal plate (of cartilage)
- Metaphysis
The growth of bone in the epiphyseal plate
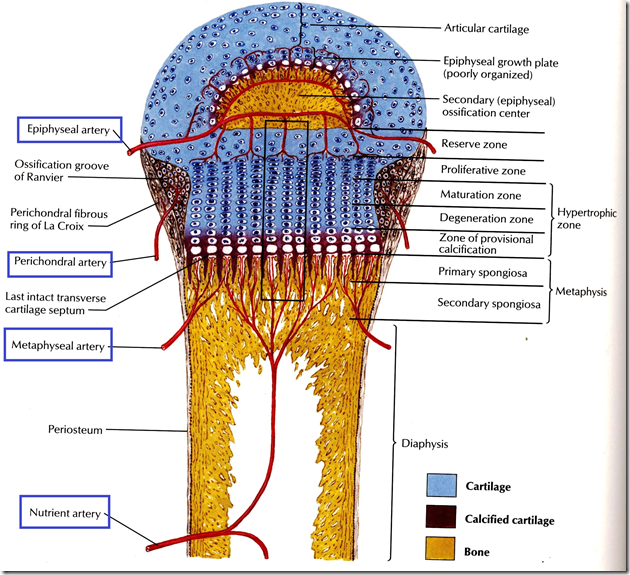
Before epiphyseal closure, Metaphysis is richly supplied with blood through end arteries forming hair-pin bends. This is a common site of osteomyelitis in children, because bacteria or emboli easily gets trap in the hair-pin bends, causing infarction.
After epiphyseal closure, the vascular communications are established between the metaphyseal and epiphyseal arteries. Therefore, osteomyelitis will not occur after epiphyseal closure, especially in adults.
Arteries supplying a developing long bone
Primary centre of ossification
- Diaphysis
- prenatal
Secondary centre of ossification
- Epiphysis
- postnatal
- chrondrocytes form cartilage
- no blood supply in cartilage so die, and then osteoblasts will calcify dead cartilage
- hyaline – articular cartilage, depends on synovial fluid to get nutrition
- when synovial fluid runs out – forms osteoarthritis
- the growing end is the end of the bone where it appears earlier but fuses later
- lower end of radius and ulnar & upper end of humerus
- lower end of femus & upper end of tibia and fibula
- importance
- amputation end is growing end (20 years or younger)
- leave an additional skin to allow the bone to grow
- or not, skin will be torn from the growing bone after amputation
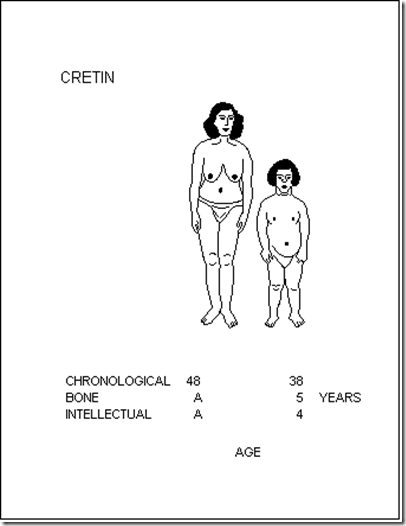
Cretin has a bone age of a 5 year old. She has a developmental abnormality.
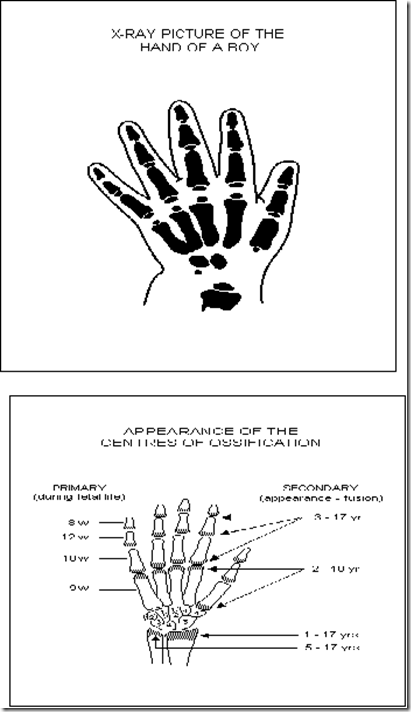
Radiologists determine the bone age by looking at xray of the wrist and teeth.
_____________________________________________________________________
Bones of Upper Limbs
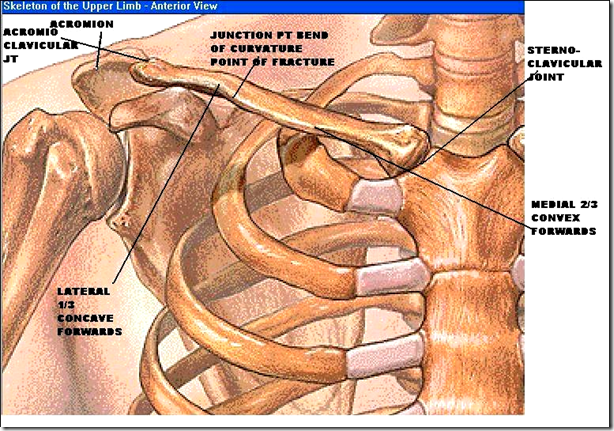
- Curvature of clavicle
- middle 2/3 & lateral 1/3
- many fractures happens here
- clavicle supported by
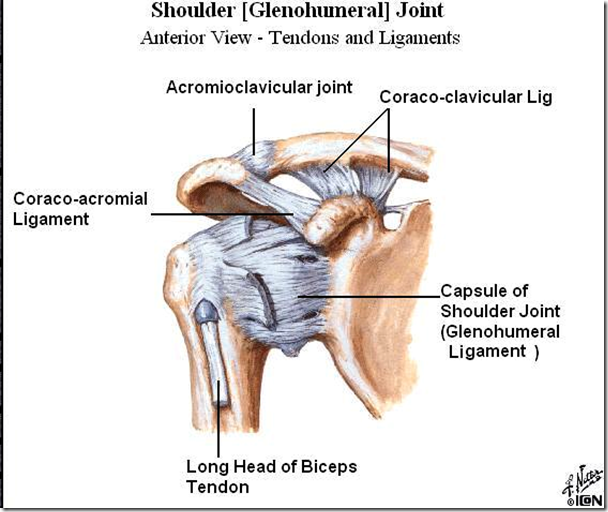
- coraco-clavicular ligament
- conoid part
- connect coracoid process with clavicle
- bears the weight of upper limbs
- so if ligament ruptured, clavicle difficult to heal
- trapezeoid part
- conoid part
- coraco-clavicular ligament
Clavicle fracture
Abduction of shoulder
- Every 3 degree abduction
- 2 degree at shoulder joint
- TOTAL (out of 180 degree): 120 degree btwn glenoid & humerus
- 1 degree scapular forward rotation at acromio-clavicular & sterno-clavicular joint
- TOTAL: 60 degree
- 2 degree at shoulder joint
- true shoulder joint
- glenohumeral joint
- coraco-acromial arch (false shoulder joint)
- coracoid process
- acromion process
- coraco-acromial ligament
- Below clavicle there is a fascia
- clavi-pectoral fascia
- strong
- pierced by cephalic vein
- between pectoralis minor muscle and clavicle
- clavi-pectoral fascia
Scapula
- Borders
- Medial border
- Lateral border
- Inferior border
- Superior border
- Angles
- Superior angle
- Inferior angle
- Fossa
- Anteriorly
- Subscapular fossa
- Supraglenoid fossa
- Glenoid fossa
- Posteriorly (relation to spine of scapula)
- Supraspinous fossa
- Infraspinous fossa
- Anteriorly
- Other parts of the scapula
- Scapular notch
- Coracoid process
- Acromion process
- Spine of scapula
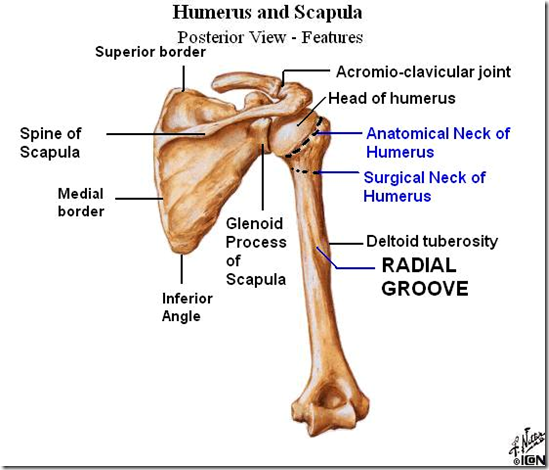
Posterior view of the humerus
- Anatomical neck
- junction point between head and tubercle
- Surgical neck
- in btwn diaphysis and head + tubercle
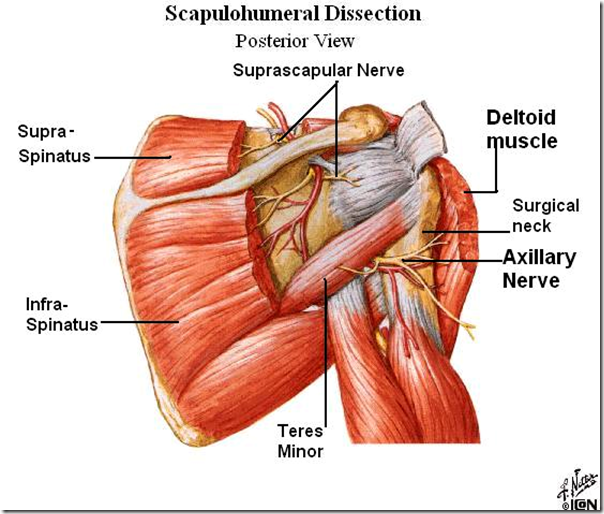
- 3 important nerve
- Axillary nerve
- surround the surgical neck
- supply the deltoid
- fracture of surgical neck/inferior dislocation of shoulder
- paralysis of deltoid
- atrophy of deltoid
- Radial nerve
- radial groove/fossa
- radial nerve runs in middle 3rd of humerus
- suffering from osteogenic sarcoma, compression of radial nerve, fracture middle 3rd of humerus, saturday night palsy (temp effect)
- extension of wrist
- paralysis due to fracture of middle 3rd of humerus
- wrist flexed always
- wrist drop
- wrist flexed always
- paralysis due to fracture of middle 3rd of humerus
- Ulnar nerve
- lies behind medial epicondyle
- intrinsic muscle of the hand
- paralysis if fracture medial epicondyle
- Axillary nerve
- Axillary nerve paralysis
- subluxtion of shoulder as loss of abduction has caused shoulder to come down under the weight of the upper limbs
- Radial nerve injury
- wrist drop
- Trochlea
- form humero-ulnar joint
- Capitulum
- forms which joint?
- Radial tuberosity
- insertion of the biceps
- flexor of elbow
- Ulnar tuberosity
- insertion of brachialis
- flexor of elbow
- Styloid process of radius always lower than styloid process of ulnar
- why?
most common fracture of upper limb at lower end of radius - altered position
- if styloid process of radius is higher
- colles fracture
- dinner fork deformity
- if styloid process of radius is higher
- why?
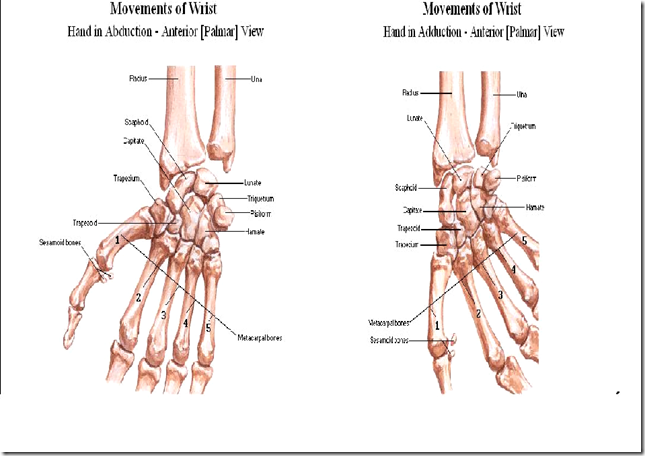
- Carpal bones
- dont need to know all the carpal bones
- not important
- What forms the wrist joints?
- lunate
- scaphoid
- triquetrum
- lower end of radius
- NOT INVOLVING ULNAR AT ALL
- dont need to know all the carpal bones
- 1st carpal-metacarpal joint (CMC joint)
- trapezium & 1st metacarpal joint
- saddle type of joint
- Ligament of flexor retinaculum, covering the
- scaphoid
- trapezium
- piciform
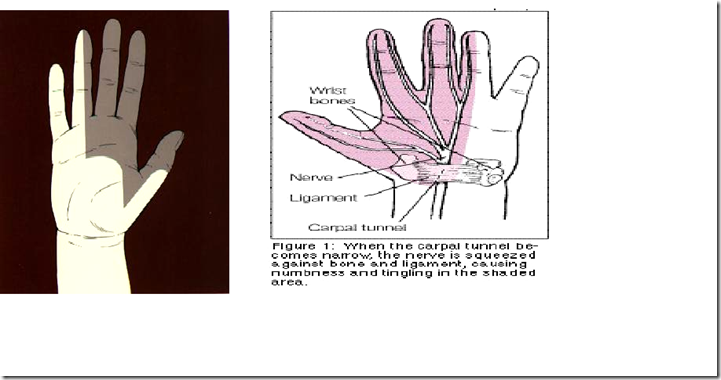
- Carpal tunnel
- in btwn flexor retinaculum ligament and the carpal bones
- All the tendons go into it
- 1 structure is compressed
- median nerve
- carpal tunnel syndrome
- loss of sensation – lateral 3 1/2 of fingers
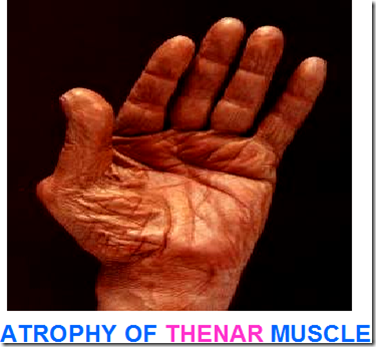
- atrophy of thenar muscle
- in btwn flexor retinaculum ligament and the carpal bones
- Carpal tunnel, loss of sensation in the shaded area
- lateral 3 1/2 of fingers
_____________________________________________________________________
Bones of the lower limbs
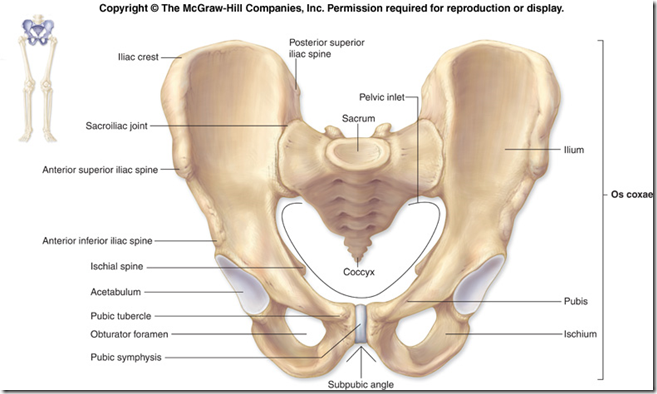
Pelvic Girdle
- Bony ring
- formed by 2 hip bones
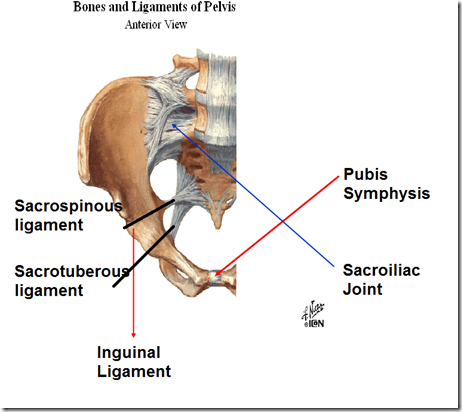
- joined at symphysis pubis & sacrum
- Symphysis pubis
- Secondary cartilaginous joint
- fibrocartilage disc
- Secondary cartilaginous joint
- Sacroiliac joint
- between sacrum and ilium
- Plane type synovial joint
- transmit weight of trunk to each femur
- weight bearing joint *
- Inguinal ligament
- between anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) & pubic tubercle
- forms fold of groin
- attachment of bony surfaces
- separates abdomen & lower limb
- between anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) & pubic tubercle
- 3 parts
- Ilium
- Ischium
- Pubis
- Relationship
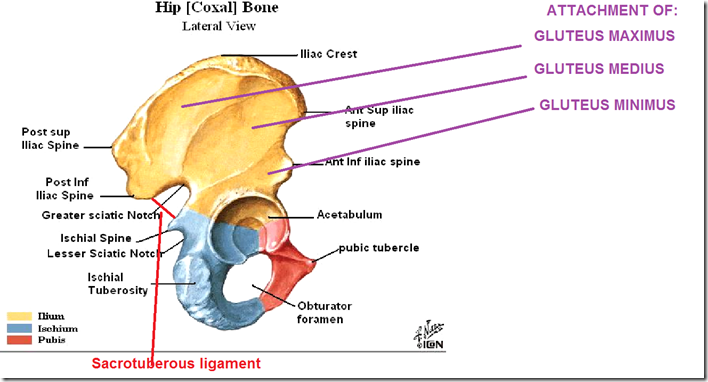
- Posterior superior iliac spine
- dimple of venus
- Anterior inferior iliac spine
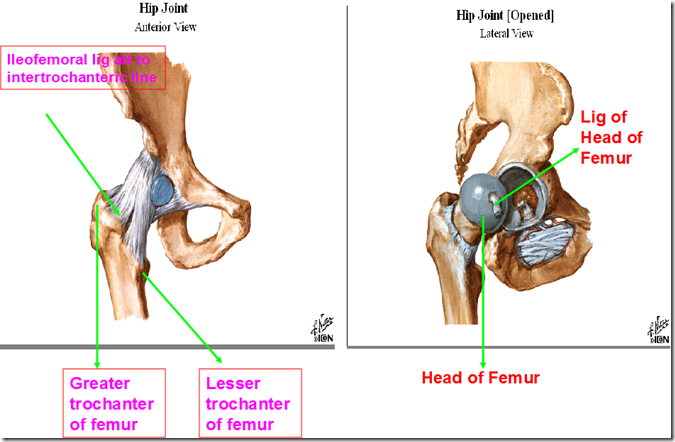
- iliofemoral ligament attachment
- strongest ligament in the body
- maintains integrity of hip joint
- especially when hip joint is injured
- iliofemoral ligament attachment
- Greater sciatic notch
- sciatic nerve runs through it
- Lesser sciatic notch
- pudendal nerve runs through it
- Sacrotuberous ligament
- important for perineal muscle – reproductive system
- Ischial tuberosity
- origin of hamstring muscles
- flexor of knee
- extensor of hip
- origin of hamstring muscles
- Gluteus maximus
- extensor of hip
- Gluteus medius
- abductors of hip
- Gluteus minimus
- abductors of hip
- Acetabulum
- covered with acetabulum labrum
- socket of hip joint
- holds head of femur
- Posterior superior iliac spine
- Greater Sciatic notch
- Becomes greater sciatic foramen by Sacro-tuberous ligament
- Through this foramen, Sciatic nerve passes down into back of thigh with:
- Superior Gluteal nerve
- Inferior Gluteal nerve
- Pudendal nerve
- reenters through lesser sciatic notch
- supplies the perineal organs
- Lesser Sciatic notch
- Contains pudendal nerve
- reenters the pelvis
- Contains pudendal nerve
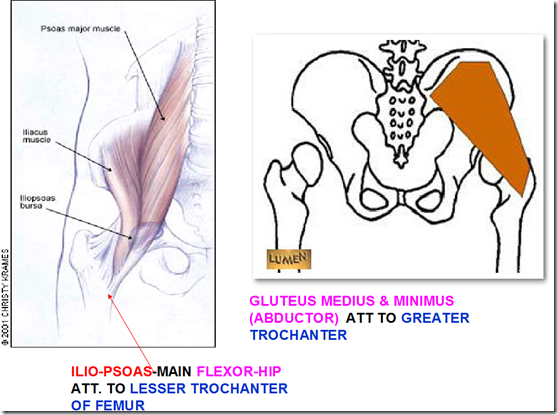
- Greater trochanter
- attaches Gluteus medius & minimus
- abductor of the hip
- intertrochanteric neck of femur fracture
- below the neck of femur
- cross the greater trochanter
- paralyses abductor muscles of the hip
- attaches Gluteus medius & minimus
- Lesser trochanter
- attaches ilio-psoas muscle
- flexor of the hip & vertebral column
- attaches ilio-psoas muscle
- Piriformis muscle
- demarcates the sciatic notch
- Above
- superior gluteal nerve & vessel
- Below
- inferior gluteal nerve & vessels
- sciatic nerve
- Above
- demarcates the sciatic notch
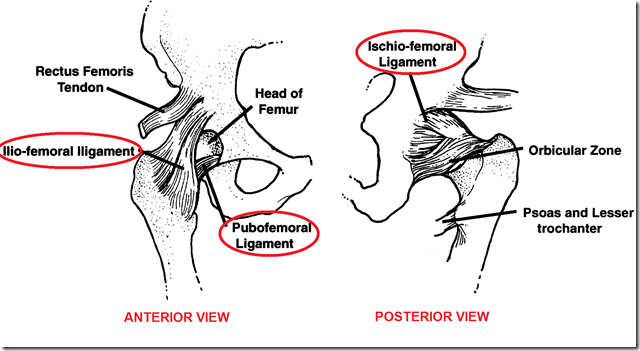
- Capsule of hip joint strengthened by
- iliofemoral ligament
- ischiofemoral ligament
- pubofemoral ligament
- therefore dislocation almost impossible
- Ligament of head of femur
- ligamentum capitis femoris
Congeniral Hip dislocation (Putti’s Triad)
- occurs in children
- 5% of OPD female
- acetabulum not formed
- head of femur displaced
- therefore there will be dislocation of the hip
Neck of femur fracture
- arteries passing through
- Neck of femur fracture
- Proximal: head of femur
- no important muscles
- not much of a problem
- Distal: total lower limbs
- shortening of lower limb
- muscle act on distal fragment
- no abduction, so only adduction
- Proximal: head of femur
- If it is a subcapital intertrochanteric fracture (distal to neck to femur)
- which is below the the neck of femur
- across the greater trochanter
- there will be avascular necrosis of the head of femur
- cut off blood supply
- paralyses abductor muscles of the hip
- gluteus medius and minimus
- which is below the the neck of femur
Limb length deformity
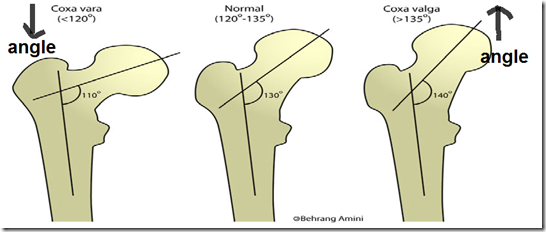
- Coxa vara
- greater the degree of coxa vara
- shorter the length of the limb
- includes all forms of decrease of the femoral neck-shaft angle to less than 120 degrees
- due to
- congenital rickets (most common)
- fibrous dysplasia
- epiphyseal injury
- greater the degree of coxa vara
- Coxa valga
- greater the degree of coxa valga
- longer the length of the limb
- deformity of the hip where femoral neck-shaft angle is usually above 135 degrees
- greater the degree of coxa valga
- Linea aspera
- only found in human
- thickened because we are bipedal
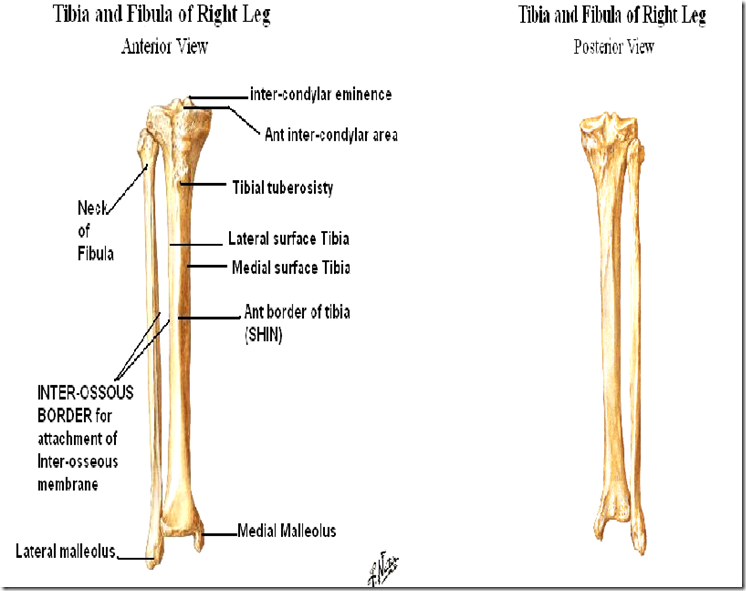
- Tibial tuberosity
- attachment point for
- quadriceps femoris muscle
- patellar ligament
- attachment point for
- What are the intra-articular structures in the knee joint?
- meniscus
- anterior & posterior crucial ligament
- attached in intercondylar fascia
Tibia & Fibula
- There is a nerve around the neck of fibula
- common peroneal nerve/common fibular nerve
- most common nerve affected in diabetic neuropathy
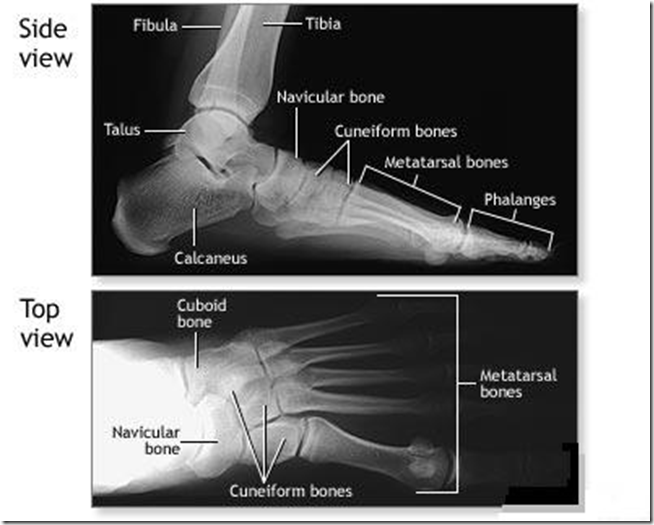
Bones of the foot
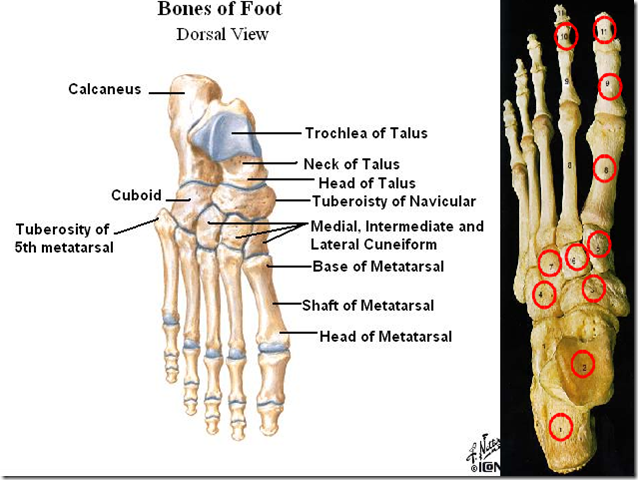
Need to know all the Tarsal bones:
- Hindfoot
- Talus
- connects to the tibia and fibula
- to form ankle joint (talocrural joint)
- parts
- trochear
- neck
- head
- connects to the tibia and fibula
- Calcaneus
- connects to talus via the subtalus joint
- Talus
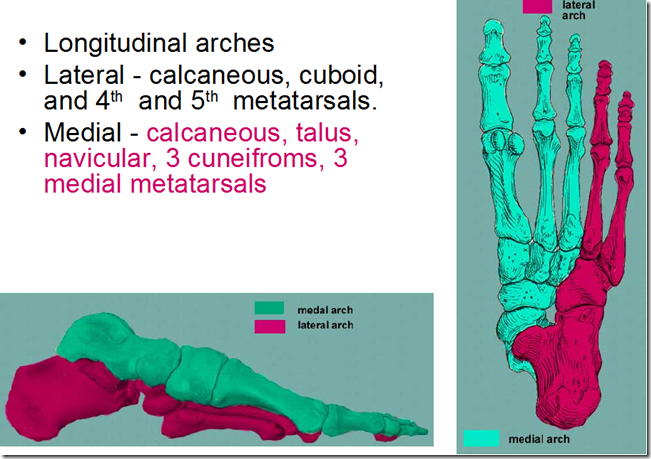
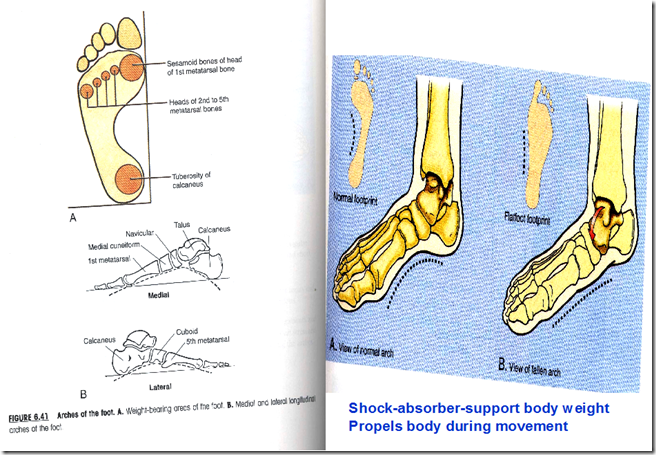
- Arches of the foot (shock absorber)
- Cuboid
- lateral
- articulates with 4th & 5th metatarsals
- Navicular
- 3 Cuneiform
- Medial, intermediate and lateral
- articulate with 1st, 2nd & 3rd metatarsals
- Cuboid
Metatarsal bones
- medial to lateral
Phalanges
- distal, medial and proximal
Arches of the foot
- Longitudinal lateral
- calcaneous
- cuboid
- 4th & 5th metatarsals
- Longitudinal medial
- calcaneous
- talus
- navicular
- 3 cuneiforms
- 1st, 2nd & 3rd metatarsals
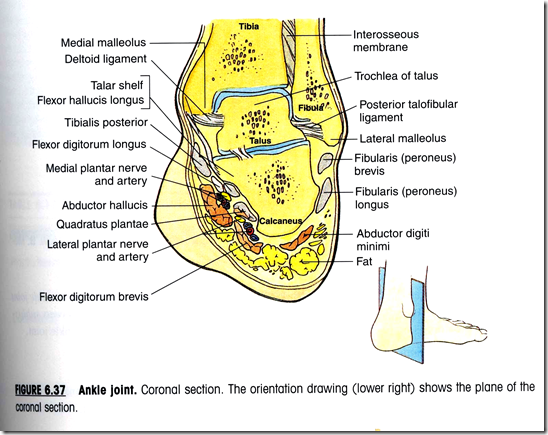
Ankle joint
Ankle joint
- Hinge joint
- formed by articulation of the talus with the malleoli of the tibia and fibula
- Trochear surface of talus
- articulates with lower end of tibia
- Comma-shaped articular surface of medial side of talus
- articulate with medial malleolus of tibia
- Triangular articular surface of lateral side of talus
- articulates with lateral malleolus of fibula
- Inferior transverse tibio-fibular ligament
- forms posterior aspect of tibio-fibular mortice
- Trochear surface of talus
- Talonavicular joint
- between navicular tarsal bone and talus
- Subtalar joint
- between talus and calcaneus
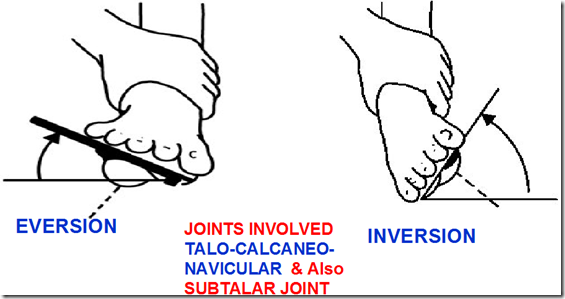
- Hallus valgus
- change of alignment of great toe
Allignment of the foot
- Pes Planus (flat foot)
- congenital
- medial longitudinal arch may be poorly developed
- difficulty in long distance walking/ running
- causes:
- weak plantar ligaments
- weak muscles
- Pes Cavus (exaggerated arch)
- associated with neurological disorders
- overactive peroneus longus
- Congenital deformities
- Talipes Equinus
- marked plantar flexion
- Talipes Varus
- foot inverted and adducted
- Talipes Valgus
- foot everted and abducte
d
- foot everted and abducte
- Talipes Equinus
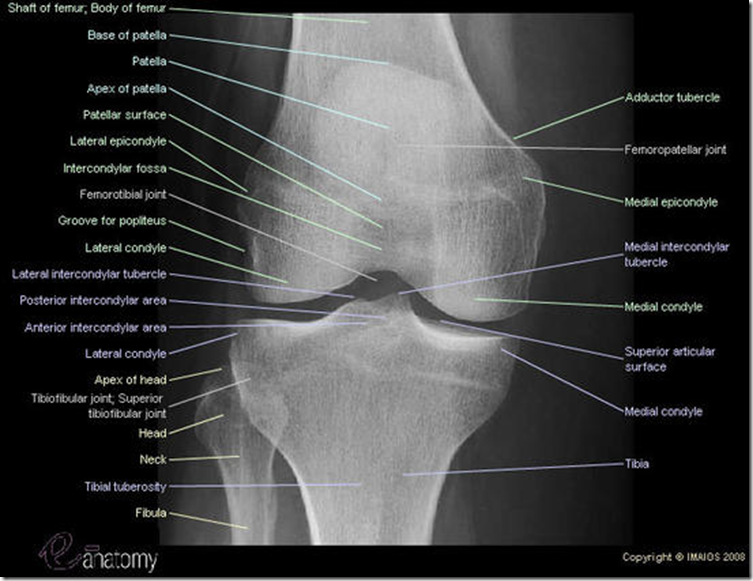
X-Ray – Learn up!



































I noticed that it’s hard to find your site in google, i found it on 16th spot, you should
create some social bookmarks to rank it in google and increase traffic. I had the same problem with my blog, your should search in google for – Insane google ranking boost – it helped me a lot