Read from foundation 1 ! Here are some of the important things to know about the female reproductive system. However, the notes are not complete. Will be updated on a later date.
Ovaries
- Functions
- produce ovum
- produce hormones (oestrogen & progesterone)
- 3 ligaments attached to it
- ovarian ligament
- suspensory ligament
- mesovarium (broad ligament)
- function: anchor the ovary, blood vessels travel thru the mesovarium
- Outer to tunica: germinal epithelium (cuboidal cells)
- continuous with peritoneum
- do not produce germ cells
- Covered with tunica albugenia
- outer cortex: ova develop here
- inner medulla: blood vessel ramify here
Development of the ovarian follicles
- primordial follicle
- simple epithelium
- primary follicle
- squamous
- secondary follicle
- stratified squamous
- versicular follicle/ Graafian follicle
- multilayer thick
- rupture –> ovulation
Corpus luteum
- of menstruation
- of pregnancy
Corpus albicans
- regressed corpus luterum
- as corpus luteum broken down by macrophages, fibroblasts lay down type 1 collagen
- may persist as a scar on surface of the ovary
Uterine tubes
- lateral to uterus
- opens to peritoneal cavity near the ovaries
- lie in the free edge of broad ligament
- mesosalpinx: cover the uterine tubes
- 4 parts:
- infundibulum
- funnel shaped
- distal end
- fimbriae catches ova
- ampulla
- widest & longest part
- fertilization
- isthmus
- narrow part
- Uterine part
- passes thru the uterine wall
- infundibulum
- Wall consists of
- circular smooth muscles
- highly folded mucosa
- ciliated cells: move oocyte
- non ciliated cells: produce secretions
- Functions:
- capture oocyte
- transport oocyte to uterus
- fertilization site
Uterus
- located in the pelvis, anterior to rectum, posterior to urinary bladder
- thick walled, hollow, muscular, lined by mucosa
- Parts
- body
- fundus
- above opening of uterine tube
- cervix
- narrow inferior 1/3 separated from the body by the isthmus
- projects into vagina
- narrow cervical canal
- internal os (project into uterine body)
- external os (project into vagina)
- Position of the uterus
- Anteverted
- angle between vagina axis & cervical axis
- Antiflexed
- angle between cervical axis & axis of the uterus
- Abnormal: retroverted, retroflexed
- Anteverted
- Supports:
- muscles
- pelvic diaphragm (levator ani msucle)
- urogenital diaphragm
- ligaments
- broad ligament
- round ligament
- lateral cervical ligament (cardinal ligament)
- uterosacral ligament
- muscles
- Uterine wall composed of 3 layers
- Perimetrium (visceral layer of peritoneum)
- Myometrium
- hypertrophy & hyperplasia during pregnancy
- Endometrium (epithelium with simple tubular glands)
- cyclic changes in response to hormones
- shed during menstruation
- 3 layers:
- stratum functionalis
- spiral arteries
- stratum basalis
- straight arteries
- contains tips of tubular glands
- do not respond to ovarian hormones
- not shed during menstruation
- formes new functional layer after menstruation
- stratum functionalis
- menstruation: spasm of spiral arteries, ischaemia, shed off.
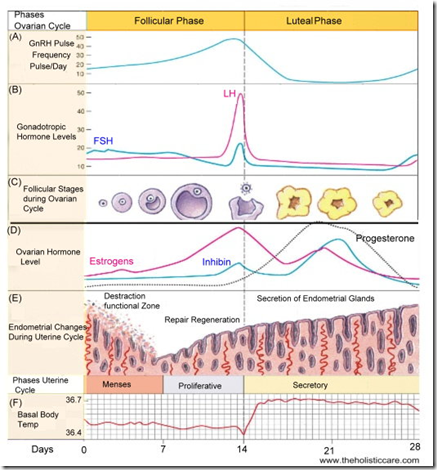
Endometrial cycle
- menstrual phase
- shedding of stratum functionalis
- proliferative phase
- stimulated by oestrogen
- epithelium starts to grow
- glands formed, straight tubules (not secretory yet)
- secretory phase
- stimulated by progesterone
- epithelium become secretory
- glands become coiled
Cervix
- less smooth muscles than body of uterus
- more of dense connective tissue
- supra vaginal part: lined by columnar epithelium with mucous glands
- mucus: acts as barrier for bacteria & lubrication of vagina
Vagina
- lined by stratified squamous epithelium
- protection
- from uterine cervix to vestibule
- direction: upwards, backwards
- vaginal fornix: recess of the upper end of vagina around the uterine cervix
- anterior
- posterior
- much deeper
- related to pouch of douglas/recto-uterine pouch
- 3 layers
- outer fibroelastic adventitia
- can expand
- muscular layer
- longitudinal smooth muscle
- mucosa
- stratified squamous epithelium
- no glands (lubricated by cervical glands)
- glycogen: metabolized by lactic acid by vaginal bacteria
- acidity prevents infection
- outer fibroelastic adventitia
External genitalia
- Mons pubis
- fatty rounded area
- labia majora
- elongated fatty skin folds
- labia minora
- fat free folds of skin
- contain erectile tissue
- vestibule
- area between labia minora
- urethra & vagina open here
- vaginal orifice covered by hymen
- greater vestibular glands are at either side of vaginal orifice in the superficial perineal space
- secretions lubricate the vulva
- clitoris
- erectile tisse
- sensitive
- hooded by prepuce
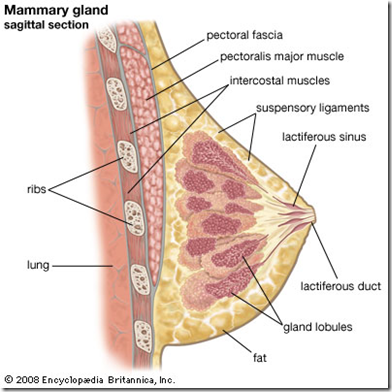
Mammary gland
- compund tubuloalveolar gland
- located in superficial fascia
- over pectoral region
- Areola: ring of pigmented skin
- with modified sebaceous gland
- nipple
- smooth muscles
- divided into 15-20 lobes by connective tissue septa
- each lobe has lobules containing secretory alveoli
- glands open to summit of nipple
- by lactiferous ducts
- secretes milk during lactation
- more ducts & fat after puberty
- more secretory unit during pregnancy & lactation
- atrophy of ducts & fat after menopause